Types of TMS Therapy: An In-Depth Look


Explore the varied types of TMS therapy and compare cbt vs psychodynamic therapy to understand their distinct advantages in treatment.
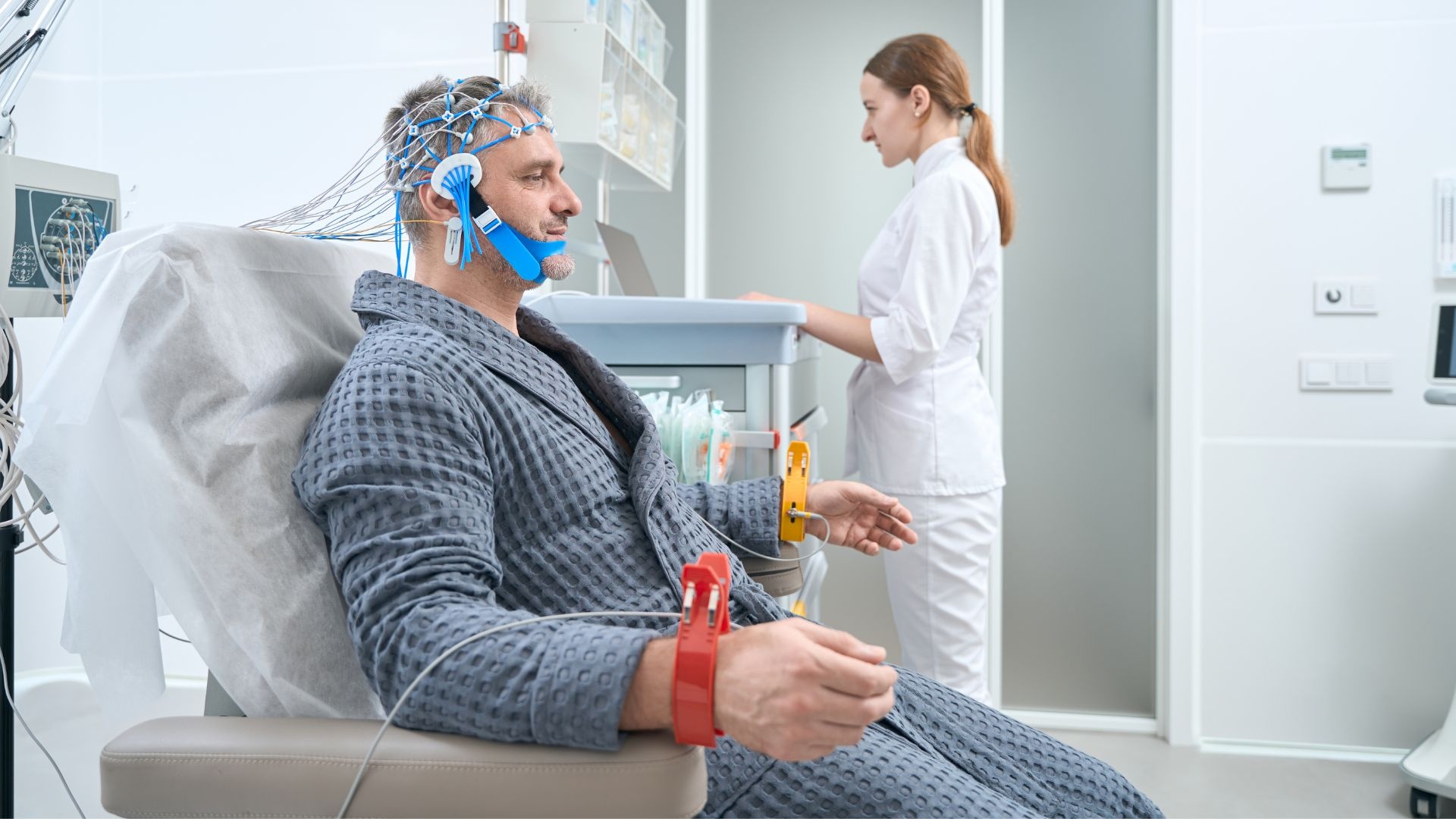
If you're feeling overwhelmed by mental health challenges and conventional therapies like CBT or psychodynamic therapy haven't been effective, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) might offer the breakthrough you need.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we focus on innovative treatments like TMS that use magnetic fields to stimulate brain activity and alleviate symptoms. In this article, we will delve into the different types of TMS therapy, exploring their potential to transform the way we approach mental health care, especially in the context of cbt vs psychodynamic therapy.
Understanding TMS Therapy
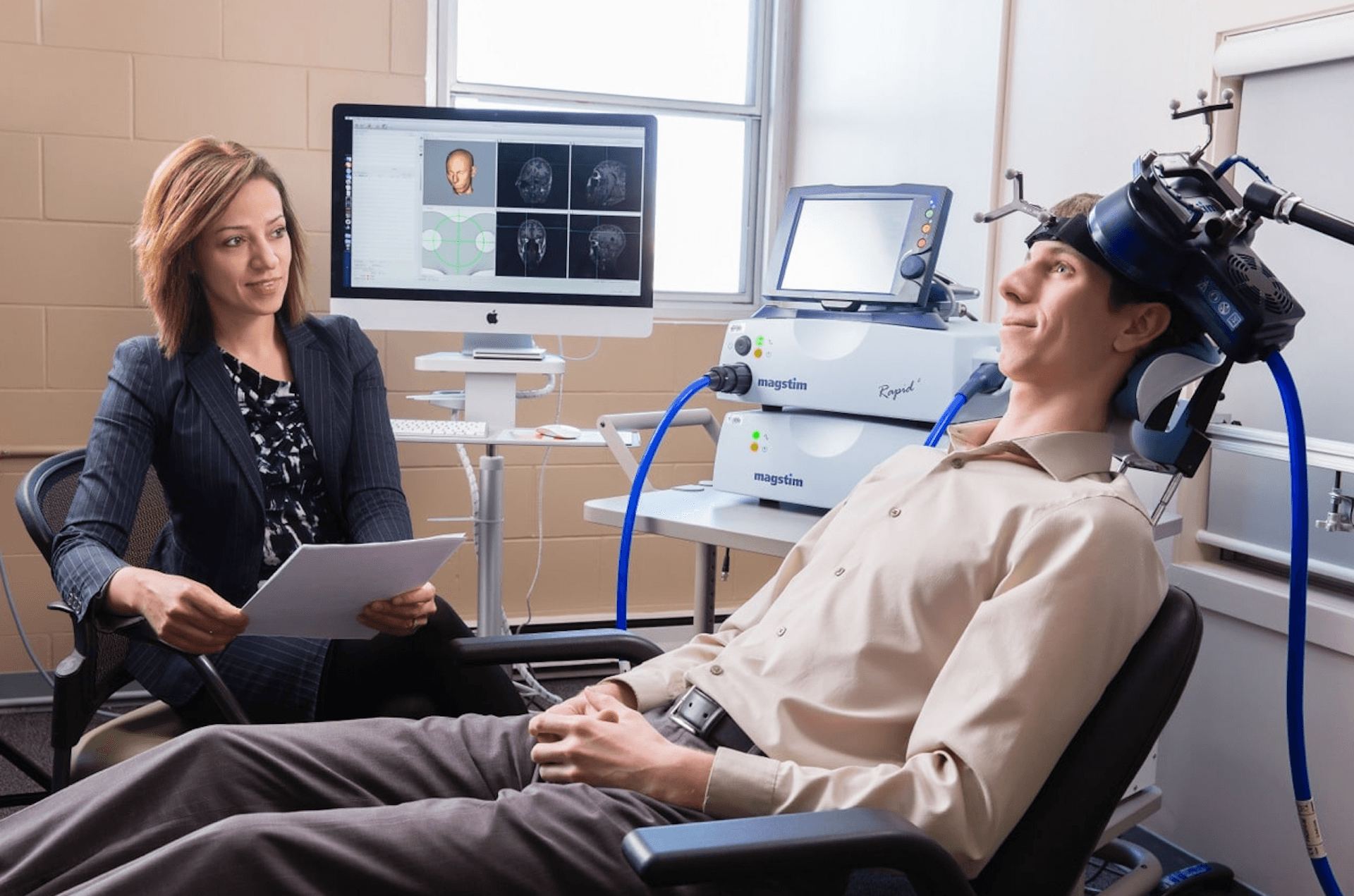
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive medical procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. It is primarily used as a treatment for major depressive disorder, particularly in cases where traditional medications and therapies have not been effective.
TMS works by placing an electromagnetic coil against the scalp near the forehead. This coil generates brief magnetic pulses, which pass easily and painlessly through the skull and into the brain.
The magnetic field induces a small electrical current in the area of the brain just under the coil, which can activate cells within the brain that are involved in mood control and depression.
Brief History and Evolution of TMS Therapy
TMS therapy was first developed in 1985 by Anthony Barker and his team in Sheffield, UK. Its therapeutic potential, particularly in neurology and psychiatry, was quickly recognized, leading to extensive research and development.
Initially, TMS was used to measure the connection between the brain and a specific muscle to diagnose damage to the pathways that control these muscles. However, researchers soon began to explore its therapeutic benefits.
The late 1990s and early 2000s marked significant milestones when clinical trials began to assess TMS as a treatment for depression.
In 2008, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved TMS as a treatment for major depression for patients who had not responded to at least one antidepressant medication. Since then, the scope of TMS has expanded, with studies exploring its effectiveness in treating a variety of conditions, including anxiety, PTSD, and certain neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease.
The evolution of TMS therapy over the years has also seen technological advancements. The introduction of different types of stimulation, like theta burst stimulation (TBS), which delivers more frequent bursts of magnetic waves, has made the treatment more effective and accessible.
Moreover, the development of deeper stimulation techniques promises to enhance the efficacy of TMS by reaching broader areas of the brain more effectively.
This brief history underscores the growing recognition of TMS as a valuable tool in the psychiatric and neurological therapeutic arsenal, offering hope to many who have not found relief through conventional methods.
Different Types of TMS Therapy
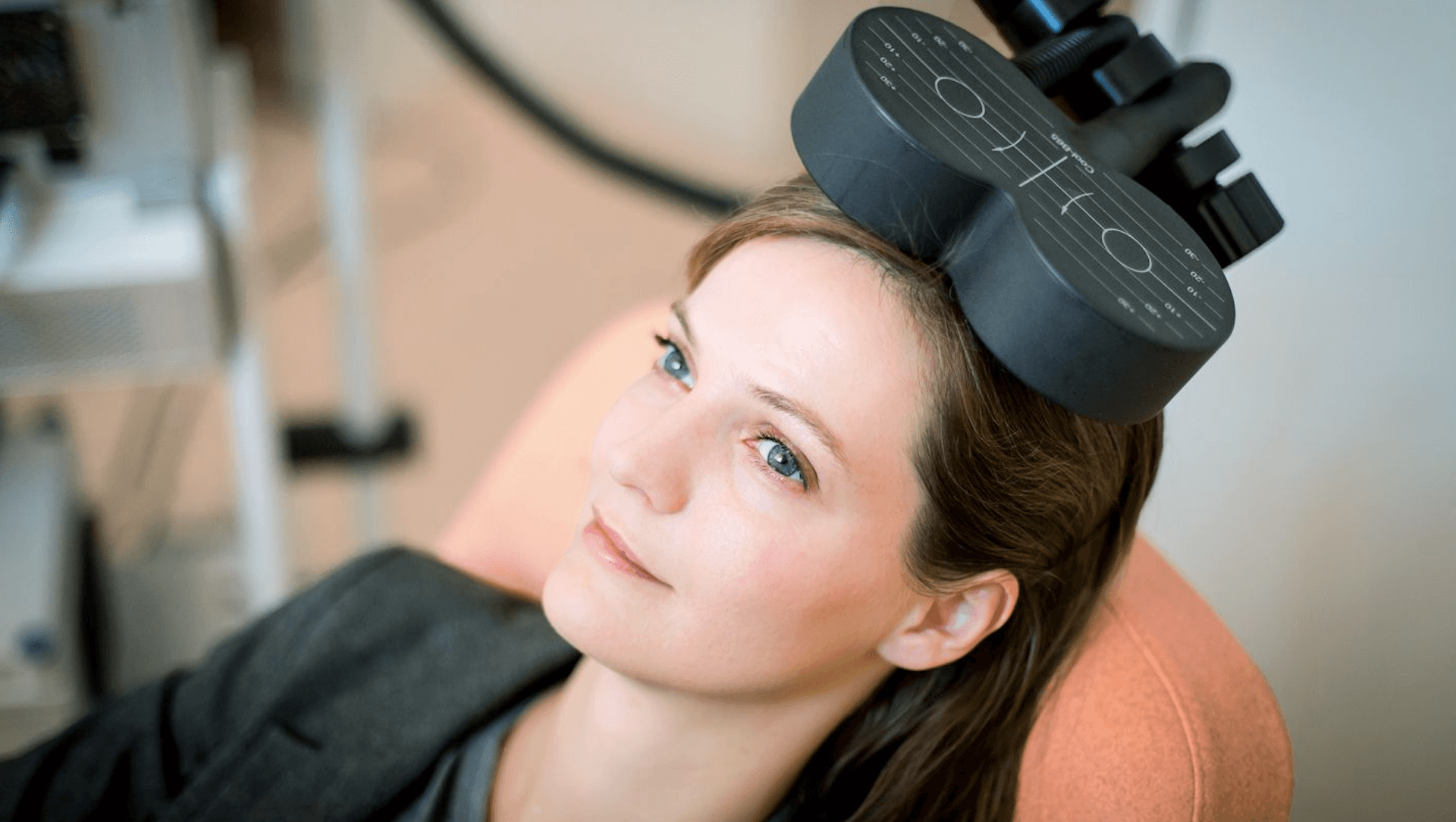

Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy offers various approaches to treating mental health disorders, each differing in intensity, application technique, and therapeutic outcomes. Here, we explore three primary types: Standard Repetitive TMS (rTMS), Deep TMS (dTMS), and Theta Burst Stimulation (TBS).
Standard Repetitive TMS (rTMS)
rTMS is the most traditional form of TMS therapy. It involves delivering magnetic pulses to the brain at a regular rate. Typically, rTMS sessions last for about 30 to 60 minutes and are conducted five days a week over four to six weeks.
The magnetic pulses are focused on specific areas of the brain associated with mood regulation and depression. rTMS is particularly noted for its effectiveness in treating major depressive disorder and has been widely researched and utilized in clinical settings.
Deep TMS (dTMS)
Deep TMS utilizes a specially designed helmet that generates a broader and deeper magnetic field, allowing it to reach deeper and larger brain areas compared to rTMS. This method is believed to enhance the stimulation's impact on the brain's neural networks involved in mood and behavior regulations.
dTMS sessions are similar in duration to rTMS but can penetrate deeper into the brain, making them potentially more effective for severe cases of depression and other mental health disorders like obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
Theta Burst Stimulation (TBS)
TBS is a newer and more advanced form of TMS that mimics the brain's natural rhythms more closely than rTMS. It delivers bursts of stimulation at a higher frequency but for a shorter duration—typically only lasting about 3 to 10 minutes per session. TBS has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of depression with fewer sessions and shorter session times, offering a more convenient treatment option for patients.
Comparison of the Types in Terms of Intensity, Duration, and Efficacy
Intensity: dTMS provides a higher intensity stimulation due to its ability to reach deeper brain regions. rTMS offers moderate intensity, while TBS uses a rapid, burst-like pattern that can trigger stronger responses in shorter periods.
Duration: rTMS requires longer session times compared to the quick sessions of TBS. dTMS sessions last similarly long as rTMS but may require fewer sessions due to its deeper penetration.
Efficacy: While all three types are effective for treating depression, dTMS and TBS might offer additional benefits for more complex or resistant cases of mental health disorders. TBS, in particular, shows promise for providing quicker symptom relief, while dTMS's extensive reach might offer advantages in treating conditions like OCD and anxiety.
These variations in TMS therapy cater to different patient needs and treatment goals, making TMS a versatile and highly customizable option in the field of mental health treatment.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
TMS Therapy Vs. Other Therapies
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) provides a unique alternative in mental health treatment, contrasting significantly with traditional therapies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and psychodynamic therapy. Below are key comparisons and distinctions:
Comparison with CBT and Psychodynamic Therapy
CBT:
Focuses on modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors to change emotional responses.
Involves structured sessions with homework and active participation.
Effective for a range of conditions like anxiety and depression.
Psychodynamic Therapy:
Aims to uncover deep-seated emotional issues from past experiences.
Involves exploring unconscious thoughts and may require long-term commitment.
Suitable for addressing complex emotional conflicts.
TMS:
Directly stimulates brain areas involved in mood regulation using magnetic fields.
Does not require verbal interaction or introspection.
Beneficial for patients resistant to or uncomfortable with talk therapies.
Effectiveness and Patient Experience
Effectiveness:
TMS provides a non-pharmacological treatment option, ideal for those who prefer to avoid medications.
Demonstrates efficacy in reducing symptoms of severe depression, particularly where CBT and psychodynamic therapy have been ineffective.
Patient Experience:
Minimal emotional and physical exertion required.
Sessions are short (20-40 minutes) and non-invasive, with no systemic side effects.
Less time-consuming compared to the lengthy sessions typical of CBT or psychodynamic therapy.
In sum, TMS therapy offers a compelling, effective alternative to conventional treatments like CBT vs psychodynamic therapy, particularly for those seeking less invasive and drug-free options. This method stands out by providing direct brain stimulation, which can be an advantageous route for individuals who have not responded well to traditional therapies.
Benefits of TMS Therapy
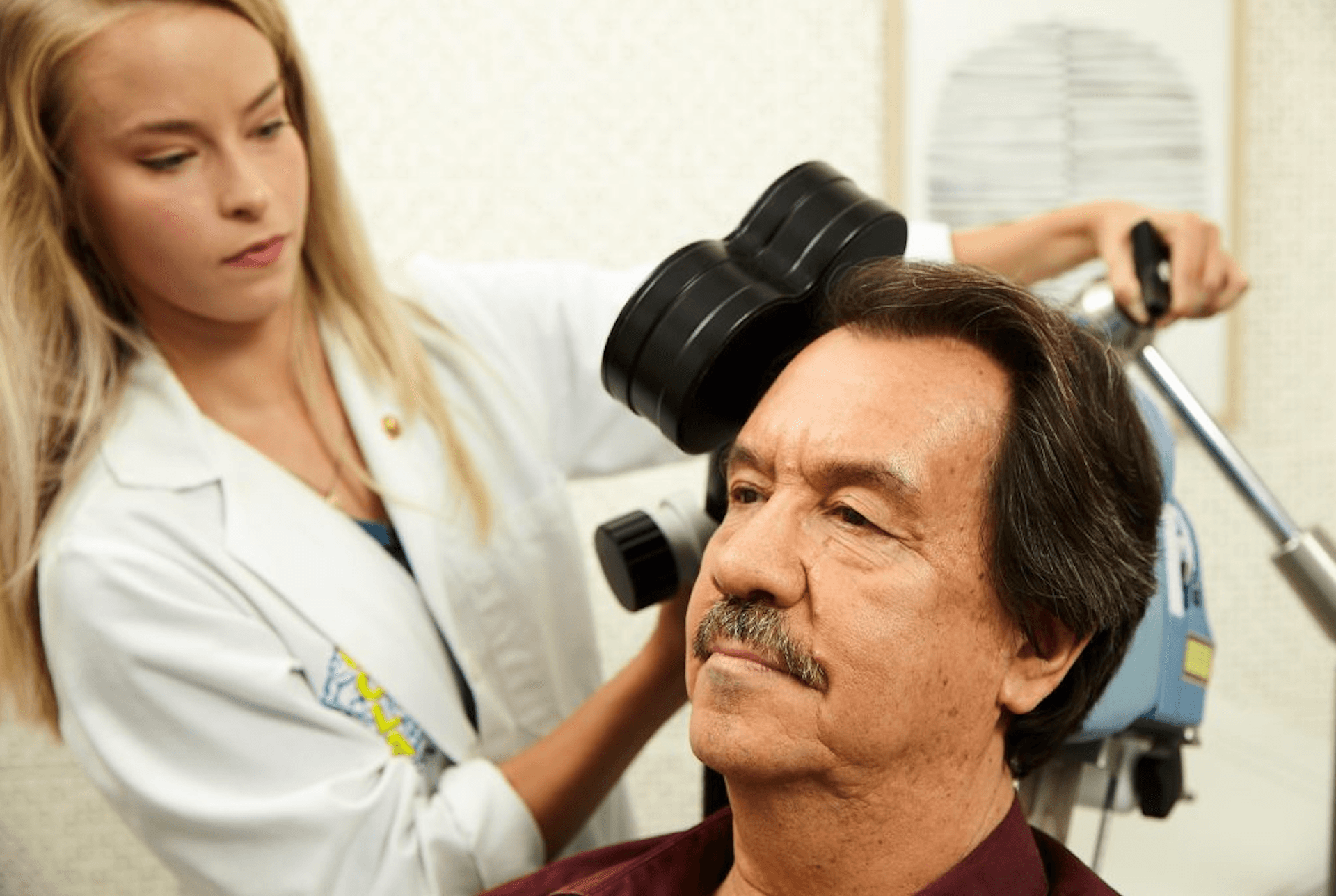
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment option, offering significant clinical benefits for individuals grappling with various mental health disorders. This section explores the extensive clinical advantages of TMS and identifies the groups most likely to benefit from this innovative therapy.
Clinical Benefits and Who Can Benefit From It
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy offers a range of clinical benefits that make it a valuable treatment option for individuals struggling with various mental health disorders. Here are some of the key clinical advantages of TMS:
Effectiveness in Treatment-Resistant Depression: TMS is particularly beneficial for individuals who have not responded to traditional treatments like antidepressants and psychotherapy.
Non-Invasive and Drug-Free: TMS does not require surgery or anesthesia, and it doesn't involve medications, making it an attractive option for those who experience negative side effects from antidepressants.
Low Side Effect Profile: Unlike many antidepressants, TMS typically results in few or no systemic side effects. The most common side effect is temporary discomfort at the treatment site during sessions.
Quick Onset of Benefits: Some patients may begin to see improvements in their symptoms within the first two weeks of starting TMS therapy, although the full effect may take several weeks.
Who Can Benefit:
Individuals with major depressive disorder, especially those who have not found relief through medications or other therapies.
Patients suffering from anxiety, PTSD, and certain neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease, where studies have shown promising results.
Those looking for a non-medication-based approach to mental health treatment.
Psychological Improvements Noted in Various Studies
Research has documented various psychological improvements in patients undergoing TMS therapy:
Improved Mood: Many patients report significant improvements in mood and general wellbeing.
Increased Cognitive Function: Studies have noted enhancements in cognitive functions such as memory and executive functioning in patients after undergoing TMS.
Reduction in Anxiety and PTSD Symptoms: TMS has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and PTSD, providing relief to patients with these conditions.
Enhanced Quality of Life: With the alleviation of symptoms, many patients experience an overall improvement in their quality of life, including better sleep patterns, higher energy levels, and improved relationships.
These benefits highlight TMS therapy as a compelling option for those who have not responded to other forms of treatment, offering new hope and improved quality of life through innovative medical technology.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
TMS: A New Horizon in Mental Health Treatment
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) stands out as a potent, non-invasive treatment for mental health disorders, particularly effective for those resistant to conventional therapies. It offers a promising future in expanding its applications to broader neurological and mental health conditions.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we're committed to guiding you on this innovative path, helping you reclaim your life from the shadows of mental health challenges. Explore TMS therapy with us and take a step towards recovery and enhanced well-being.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772





