CBT: Techniques, What It Treats, & How It Works


Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a proven strategy for managing and overcoming depression, anxiety, PTSD, and addiction. It helps modify harmful thought patterns, enabling better distress management. Learn more about the applications of CBT and how it works — and if you or a loved one are ready to heal or recover, contact The Forge Recovery Center today.
What Is CBT?
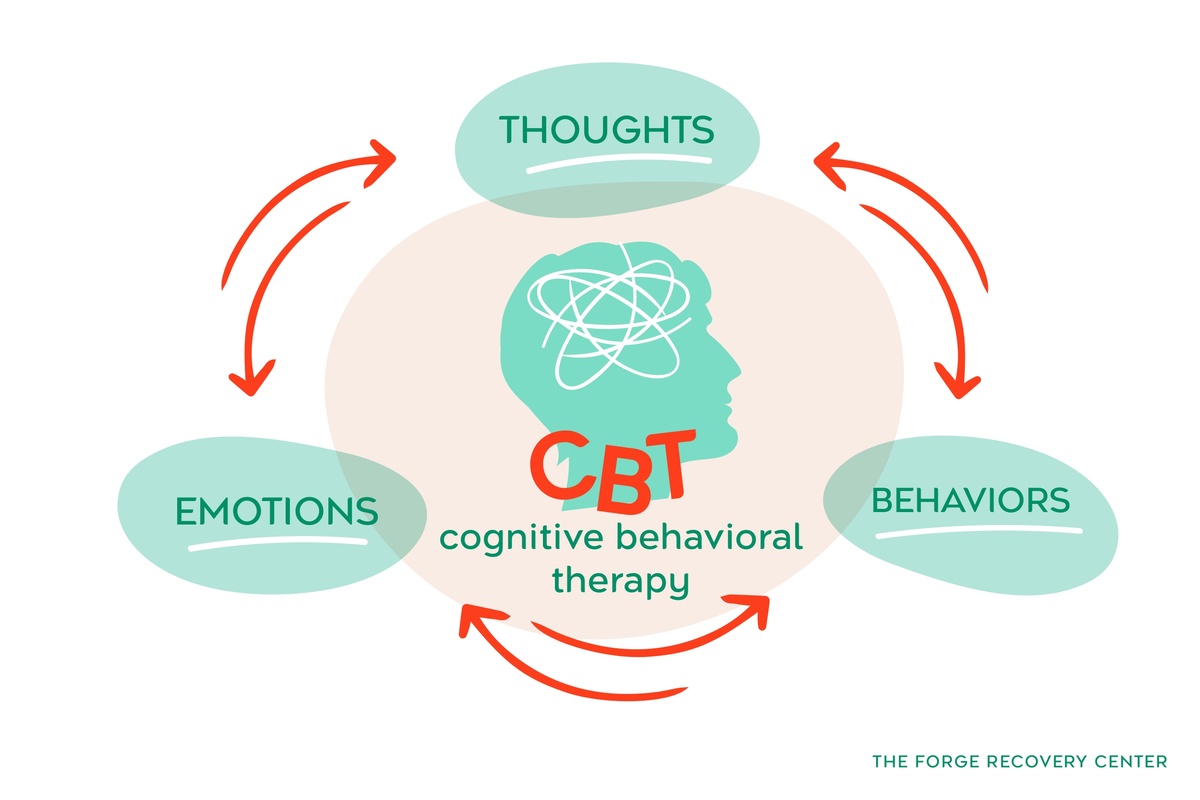
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected, and by changing our thoughts, we can ultimately change how we feel and behave.
CBT is often used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, such as:
Anxiety
Depression
PTSD
The therapy is typically short-term and goal-oriented, with patients learning practical skills to help them manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
CBT Vs. DBT
When comparing CBT and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), it's crucial to understand their distinctive approaches. CBT primarily focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. On the other hand, DBT emphasizes accepting your emotions while also working on changing them.
The unique feature of CBT lies in its structured sessions that target specific issues such as anxiety or depression through cognitive restructuring techniques. In contrast, DBT incorporates mindfulness practices alongside emotion regulation strategies to address intense emotions and improve interpersonal relationships.
In various scenarios, CBT is commonly used for treating conditions like phobias, OCD, and PTSD by challenging irrational thoughts and beliefs. Conversely, DBT is particularly effective for individuals struggling with borderline personality disorder due to its emphasis on emotional regulation skills.
Here are some key differences between CBT and DBT:
CBT focuses on changing negative thought patterns, while DBT emphasizes accepting emotions while working on change.
CBT involves structured sessions targeting specific issues; DBT incorporates mindfulness practices and emotion regulation strategies.

What Does CBT Treat?
CBT can treat a wide range of psychological conditions, as well as substance use disorders. This includes anxiety disorders, mood disorders like depression, PTSD, OCD, and addiction to illicit or prescription drugs and alcohol. Here’s an overview of common conditions treated by CBT, but keep in mind this isn’t an exhaustive list:
Mental Health Conditions
Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders manifest through persistent worry, fear, and physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat. CBT helps challenge negative thought patterns causing anxiety, fostering coping skills.
Symptoms include excessive worrying and panic attacks.
CBT teaches relaxation techniques and gradual exposure to feared situations.
Cognitive restructuring assists in changing distorted thinking patterns.
Depression
Depression is characterized by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest. CBT can aid in identifying negative thought cycles and promoting positive behaviors.
Key features are low mood, lack of energy, and changes in sleep/appetite.
CBT targets negative beliefs and encourages behavioral activation.
Behavioral activation involves scheduling enjoyable activities to boost mood.
PTSD
PTSD stems from experiencing traumatic events leading to flashbacks, nightmares, and emotional numbness. CBT addresses trauma memories and promotes adaptive coping strategies.
Symptoms include hypervigilance, avoidance, and intrusive memories.
Exposure therapy helps confront traumatic memories in a safe environment.
CBT equips individuals with the skills to manage triggers effectively.
OCD
OCD entails obsessions (intrusive thoughts) and compulsions (repetitive behaviors). CBT focuses on challenging obsessions and reducing compulsive rituals.
Common manifestations involve excessive hand washing or checking behaviors.
CBT employs exposure therapy to confront feared situations gradually.
Exposure to response prevention aids in breaking the cycle of obsessions and compulsions.
Substance Use Disorders
Substance use disorders have detrimental effects on individuals' lives due to dependency, withdrawal symptoms, and impaired decision-making. CBT targets underlying issues contributing to addiction and is a crucial part of the overall treatment plan.
CBT helps individuals identify triggers leading to substance abuse.
It emphasizes developing coping mechanisms to prevent relapse.
Relapse prevention strategies in CBT focus on recognizing early warning signs.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
How Does CBT Work?
The stages and goals of CBT are typically to rewire harmful thought patterns, modify maladaptive behaviors, and potentially improve problem-solving skills. Here’s how CBT works toward those positive changes:
Changing Thought Patterns
When engaging in CBT, it's crucial to recognize and challenge negative thought patterns. By identifying these distortions, you can begin the process of cognitive restructuring. This involves replacing irrational thoughts with more balanced and realistic ones.
For instance, common cognitive distortions include black-and-white thinking and catastrophizing. To address these, you can practice techniques like examining evidence for and against your thoughts or considering alternative explanations.
Altering Behaviors
In CBT, modifying maladaptive behaviors is key to fostering positive change. Through behavior activation, you can increase engagement in rewarding activities while decreasing avoidance behaviors. This helps in combating issues like depression and anxiety.
Reinforcement techniques play a vital role in facilitating behavior change. By implementing strategies such as positive reinforcement for desired behaviors, you can strengthen new adaptive patterns over time.
Improving Problem-Solving Skills
Effective problem-solving skills are essential for managing challenges in daily life. In CBT, the focus lies on developing practical strategies to tackle problems systematically. Problem-solving therapy within CBT involves steps like defining the issue, generating solutions, evaluating options, and implementing a plan.
You can enhance your problem-solving skills through training exercises such as brainstorming solutions, breaking down complex problems into smaller parts, and evaluating the outcomes of different approaches.
CBT Techniques
There are a number of techniques that therapists can utilize in cognitive-behavioral therapy, from journaling and role-playing to cognitive restructuring — the latter of which is arguably the primary goal of CBT. Here’s a quick overview of these techniques:
Journaling
When journaling in CBT, you can benefit from increased self-awareness and reflection on your thoughts and emotions. Different types of journaling techniques include gratitude journals, thought records, and mood tracking. To start journaling for therapy, set aside a few minutes daily to write down your thoughts and feelings. Maintain consistency by making it a part of your routine.
Role Playing
In role-playing, individuals can practice new behaviors in a safe environment, helping them improve social skills and communication. For instance, role-playing scenarios like job interviews or conflict resolution can enhance assertiveness and problem-solving abilities. By stepping into different roles, you can gain insights into alternative perspectives and responses.
Goal-Setting
Setting specific and achievable goals is crucial in CBT to track progress effectively. Use the SMART criteria—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound—to create goals that are clear and attainable. To set goals successfully, break them down into smaller tasks, establish deadlines, and regularly review your progress to stay motivated.
Guided Discovery
In guided discovery, therapists ask probing questions to help clients explore their beliefs and behaviors. By delving deeper into underlying thoughts and emotions, individuals can uncover patterns that contribute to their challenges. Questions like "What evidence supports this belief?" or "How does this thought make you feel?" facilitate self-reflection and insight.
Stress Management
Stress can significantly impact mental health; thus, learning effective stress management techniques is essential in CBT. Practices such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress levels. Incorporate stress-relief activities into your daily routine to promote emotional well-being.
Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring involves identifying negative thought patterns and replacing them with more balanced perspectives. By challenging cognitive distortions like black-and-white thinking or catastrophizing, individuals can reframe their thinking positively. Engage in exercises such as examining evidence for negative thoughts or creating alternative interpretations to promote cognitive flexibility.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy in CBT involves gradually confronting feared situations to reduce anxiety responses over time. By facing fears in a controlled manner, individuals can learn that their perceived threats are not as harmful as anticipated. The systematic exposure process enables individuals to build confidence and resilience in managing phobias effectively.
Mindfulness Training
Mindfulness plays a significant role in CBT by enhancing self-awareness and emotional regulation skills through present-moment focus. Mindfulness exercises like body scans or mindful breathing can cultivate a non-judgmental awareness of thoughts and sensations. Practice mindfulness regularly to develop a greater sense of calmness and clarity in daily life.
Breathing Exercises
In managing anxiety and stress, breathing exercises are valuable tools for promoting relaxation and reducing physiological arousal. Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing or box breathing help regulate breathing patterns during moments of distress. Follow step-by-step instructions to practice breathing exercises whenever you feel overwhelmed or anxious.

Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
The Benefits of CBT
Regular cognitive-behavioral therapy is a foundational treatment modality, with its effectiveness and range of applications speaking to its power. If you’re managing a mental health disorder or a substance addiction, CBT could be your guide toward mental well-being, true emotional health, and positive behavioral change. Here’s a summary of the core benefits of CBT:
Psychological Well-Being
Psychological well-being refers to your overall mental state encompassing emotions, thoughts, and behavior. It comprises components like self-acceptance, positive relationships, autonomy, environmental mastery, personal growth, and purpose in life. To enhance psychological well-being through CBT, you can focus on challenging negative thoughts, practicing mindfulness, engaging in positive activities, setting achievable goals, and improving problem-solving skills.
Factors contributing to psychological well-being include genetics, life experiences, social support systems, coping strategies, and resilience levels. By actively participating in CBT sessions and exercises tailored to address your specific concerns or issues, you can effectively manage stressors and develop healthier coping mechanisms. This therapeutic approach empowers you to build emotional resilience and navigate challenges with a more positive mindset.
Emotional Health
Emotional health plays a crucial role in your overall mental well-being as it influences how you perceive and respond to situations. CBT helps improve emotional regulation by teaching you how to identify and challenge irrational beliefs or distorted thinking patterns that contribute to negative emotions. Through cognitive restructuring techniques and emotion-focused interventions, you can learn to manage anger, anxiety, sadness, or other intense feelings effectively.
Managing emotions involves recognizing triggers that lead to emotional reactions and developing adaptive responses. With the help of CBT strategies such as relaxation techniques, cognitive reframing exercises, and behavioral experiments, you can cultivate emotional resilience and cope with stressors more constructively across various contexts. By applying these tools consistently in daily life situations, you can regulate emotions better and maintain mental balance.
Behavioral Changes
In CBT, making sustainable behavioral changes involves identifying maladaptive behaviors linked to negative thoughts or emotions. By creating behavior change plans that outline specific goals, action steps, timelines for implementation, and methods for monitoring progress regularly, you can track improvements effectively. For instance, you might set a goal of reducing procrastination by breaking tasks into smaller steps or using time management techniques like the Pomodoro method.
Implementing new behaviors requires practice and persistence to replace old habits with healthier alternatives gradually. Through exposure therapy, you can confront fears or phobias systematically while building confidence in managing challenging situations. By incorporating positive reinforcements, you can reinforce desired behaviors positively and motivate yourself to continue making progress towards long-term behavioral changes.
CBT Success & Statistics
Research shows that CBT is an effective treatment modality for anxiety, depression, PTSD, and OCD, even helping to mitigate the risk for relapse. Below, we’ve gathered some recent data on CBT’s efficacy to keep you informed:
Research Findings
When considering CBT, research shows its effectiveness in treating various mental health conditions. Studies indicate that CBT is particularly beneficial for anxiety disorders, depression, PTSD, and OCD. The structured nature of CBT helps individuals identify negative thought patterns and develop coping strategies.
Positive Outcomes & Statistics
Compared to other treatment approaches, CBT has shown promising results. Statistics reveal that approximately 75% of people who undergo psychotherapy like CBT experience lasting benefits. Moreover, studies suggest that the effects of CBT are long-lasting, reducing the risk of relapse in conditions like depression and anxiety.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Starting CBT
Once you’ve decided to start CBT, you’ll have to call a mental health professional for an initial assessment. You can also seek therapy at an inpatient or outpatient treatment center, or full addiction treatment if you’re facing a dual diagnosis for mental health and substance use. Here are our tips for getting started:
Finding a Therapist
When seeking a CBT therapist, research local providers through online directories or recommendations from trusted sources. Look for therapists with specific training in cognitive behavioral therapy.
Consider the importance of therapist-client fit; a strong relationship can enhance the effectiveness of CBT. Compatibility in communication styles and personalities is crucial for progress.
Ensure your potential therapist holds relevant credentials such as a license in psychology or counseling. Experience working with issues similar to yours is also vital.
Treatment Centers
Explore treatment centers that offer comprehensive CBT services, including individual and group therapy sessions. These centers often provide specialized programs tailored to different mental health conditions.
Receiving treatment at a specialized center offers structured care plans designed by experts in cognitive behavioral therapy. This approach can lead to more focused and effective treatment outcomes.
When selecting a treatment center, consider factors like location, cost, and the specific programs offered. Choose a center that aligns with your preferences and individual needs for personalized care.
Closing Thoughts
Now that you understand the ins and outs of CBT, you're equipped with valuable knowledge to make informed decisions about your mental health. With its tailored techniques and proven success rates, CBT offers a practical approach to addressing various challenges you may face. By incorporating CBT into your mental health journey, you can gain valuable skills to navigate life's ups and downs more effectively.
Take the first step towards enhancing your well-being by exploring how CBT can benefit you. Whether you're dealing with anxiety, depression, or simply seeking personal growth, CBT could be the key to unlocking a healthier mindset. Embrace the opportunity to invest in yourself and discover the transformative power of CBT.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
CBT for Mental Health & Addiction: Call The Forge Recovery Center Today!
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is a widely known and proven tool for addressing depression, anxiety, PTSD, and addiction. If you or someone you care about is grappling with these challenges, The Forge Recovery Center is ready to assist. Our team of mental health and treatment professionals, all experts in CBT, will provide a personalized therapeutic experience tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Reach out to us today to understand more about our CBT services and how they can aid in your journey towards healing.



