TMS Therapy Vs. Neurofeedback Which Is More Effective


TMS therapy vs. neurofeedback— which works best for mental health? Compare effectiveness, benefits, and differences while exploring cbt vs somatic therapy.
Facing mental health challenges, addiction, or substance abuse can be overwhelming, and finding effective treatments is crucial. Emerging therapies like Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Neurofeedback offer promising alternatives to traditional methods.
Understanding their differences and effectiveness is essential for making informed decisions about your recovery journey. In this article, we will compare TMS Therapy and Neurofeedback, providing insights to help you determine which treatment may be more effective for your specific needs.
Understanding TMS Therapy
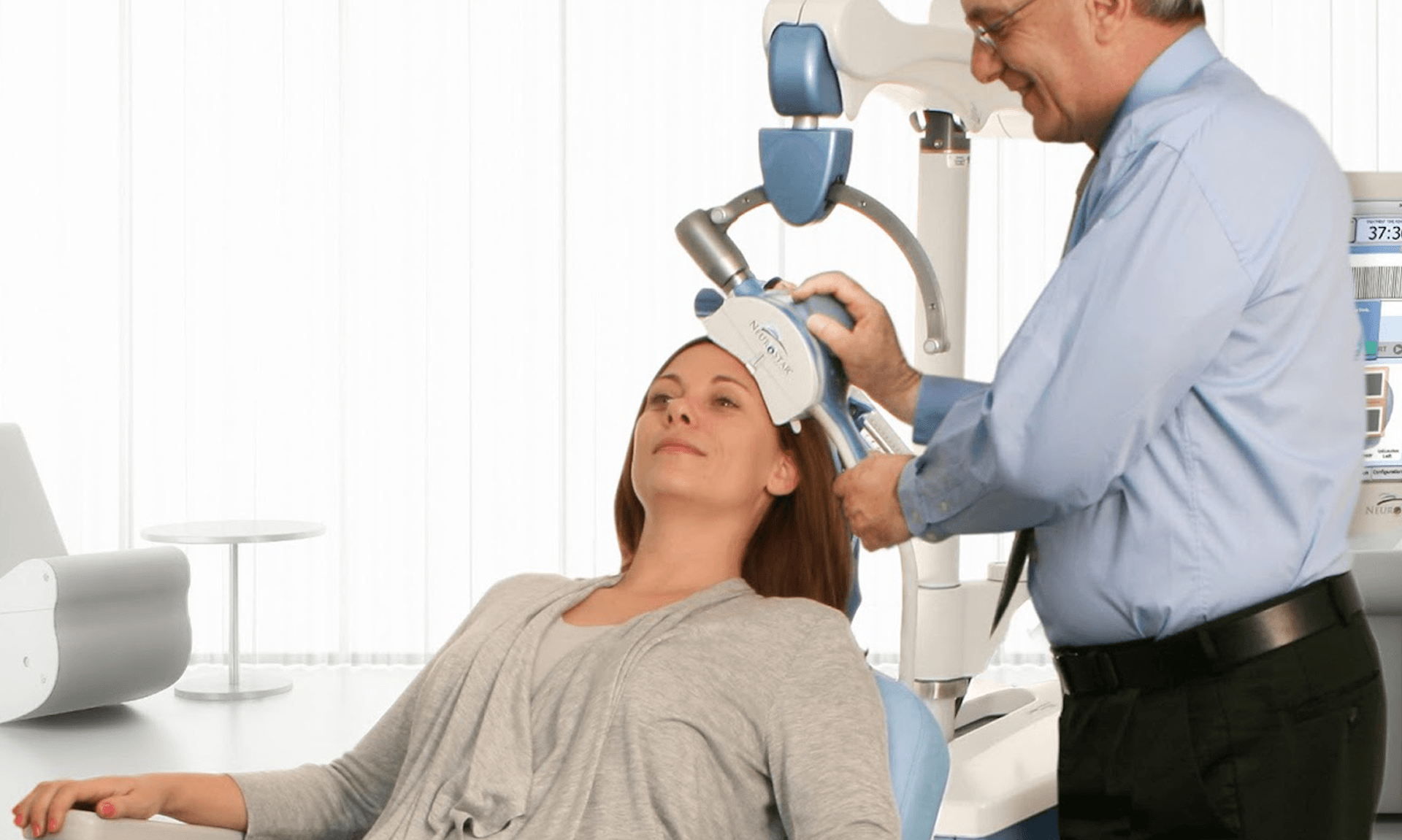
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive procedure that utilizes magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. By placing an electromagnetic coil against the scalp, TMS delivers magnetic pulses that induce electrical currents in targeted brain regions, modulating neuronal activity. This modulation can help alleviate symptoms of various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Applications
TMS has received FDA approval for several therapeutic applications:
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Approved in 2008, TMS is used to treat patients with depression who have not responded to traditional treatments.
Migraine Headaches: In 2013, the FDA expanded TMS approval to include the treatment of pain associated with certain migraine headaches.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): In 2018, TMS was approved as an adjunct therapy for adult patients with OCD.
Procedure
A standard TMS treatment involves the following steps:
Preparation: The patient is seated comfortably, and an electromagnetic coil is positioned against their scalp, typically over the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.
Stimulation: The device generates magnetic pulses that pass through the skull to stimulate nerve cells in the targeted brain area.
Session Duration and Frequency: Each session usually lasts about 20 to 40 minutes. Treatment is commonly administered five times per week over a period of four to six weeks, though this can vary based on individual needs and specific protocols.
TMS is generally well-tolerated, with patients remaining awake and alert during the procedure. Some individuals may experience mild scalp discomfort or headaches, which typically diminish over subsequent sessions.
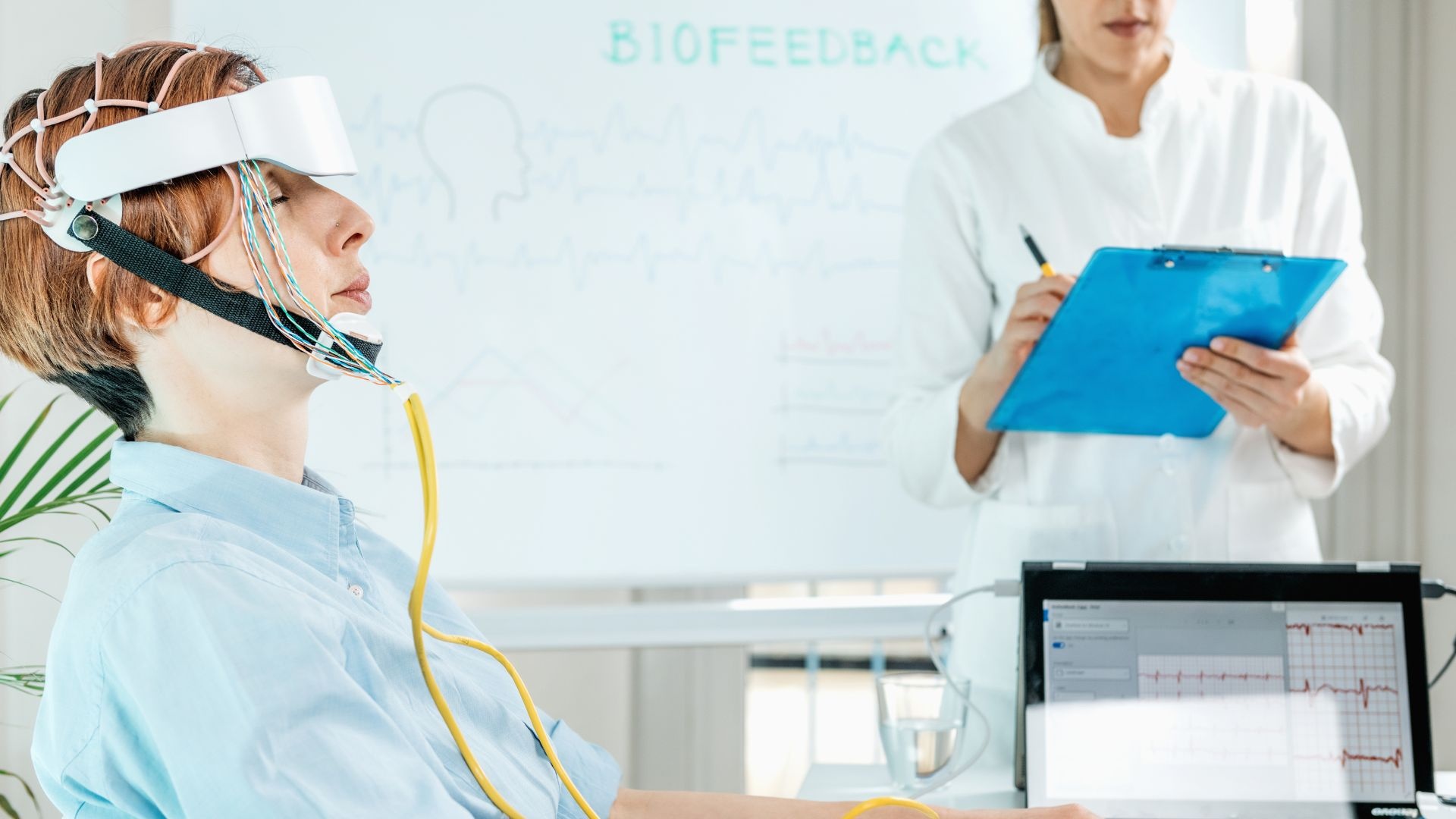
Understanding Neurofeedback

Neurofeedback, also known as EEG biofeedback, is a non-invasive therapeutic technique that trains individuals to self-regulate their brain activity. By monitoring brainwaves in real-time, neurofeedback provides immediate feedback, enabling individuals to modify their brainwave patterns to achieve desired mental states. This process enhances self-control over brain functions, promoting improved mental health and cognitive performance.
Applications
Neurofeedback has been applied to a variety of conditions, including:
Anxiety Disorders: By training individuals to increase alpha waves or other brain wave patterns associated with calm and relaxation, neurofeedback helps in managing anxiety.
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Research supports the use of neurofeedback for cognitive enhancement in individuals with ADHD, with training associated with improvements in working memory, attention, and executive function.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Neurofeedback has been explored as a therapeutic tool to help individuals with PTSD manage symptoms by promoting self-regulation of brain activity.
Procedure
A typical neurofeedback session involves the following steps:
Preparation: The individual is seated comfortably, and electrodes are placed on the scalp to measure electrical signals produced by the brain.
Monitoring: These electrodes detect brainwave activity, which is then processed by a computer to provide real-time feedback.
Feedback: The individual receives feedback through visual, auditory, or tactile cues, allowing them to learn and modify their brainwave patterns.
Training: Through repeated sessions, individuals practice adjusting their brain activity, aiming to reinforce desired patterns associated with improved cognitive and emotional states.
The number of sessions required varies based on the individual's condition and goals, but consistent practice is key to achieving lasting results.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Comparing Effectiveness
When evaluating Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Neurofeedback, it's essential to consider their treatment scopes, mechanisms, durations, and safety profiles.
Scope of Treatment
TMS: Primarily FDA-approved for treating Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and certain migraine headaches.
Neurofeedback: Applied to a broader range of conditions, including anxiety, ADHD, and PTSD.
Mechanism of Action
TMS: Utilizes magnetic fields to directly stimulate specific brain regions, modulating neuronal activity to alleviate symptoms.
Neurofeedback: Employs real-time monitoring to train individuals in self-regulating their brain activity, promoting desired mental states.
Duration and Commitment
TMS: Typically involves daily sessions over several weeks, with each session lasting about 20 to 40 minutes.
Neurofeedback: Requires multiple sessions, often 30 to 40, with the total number varying based on individual progress and specific conditions.
Side Effects and Safety
TMS: Generally well-tolerated; potential side effects include headaches and scalp discomfort.
Neurofeedback: Considered safe with minimal reported side effects, as it involves monitoring and feedback without direct brain stimulation.
Integration with Other Therapies

Integrating Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Neurofeedback with traditional therapies can enhance treatment outcomes for individuals facing mental health challenges, addiction, and substance abuse.
Combining with Traditional Therapies
Both TMS and Neurofeedback can complement established therapeutic approaches:
TMS and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Combining TMS with CBT addresses both neurological and psychological aspects of conditions like depression. TMS modulates brain activity, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of CBT by creating a more receptive mental state.
Neurofeedback and Somatic Therapy: Neurofeedback trains individuals to regulate their brain activity, which can reduce physiological symptoms of anxiety and PTSD. When combined with Somatic Therapy, which focuses on bodily sensations to process trauma, this integration fosters comprehensive healing by addressing both mind and body.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Recognizing that each individual's experience with mental health and addiction is unique, personalized treatment plans are essential. Tailoring interventions to individual needs ensures a holistic approach, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we emphasize creating customized plans that may incorporate TMS, Neurofeedback, traditional therapies, and other modalities to address the specific challenges faced by our clients.
By integrating these innovative therapies with conventional approaches, we aim to provide comprehensive care that supports lasting recovery and mental well-being.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Considerations for Choosing Between TMS and Neurofeedback
Selecting the appropriate treatment between Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Neurofeedback involves evaluating several key factors:
Individual Needs and Conditions
Specific Mental Health Conditions: TMS is FDA-approved primarily for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and certain migraine headaches. Neurofeedback, on the other hand, is applied to a broader range of conditions, including anxiety, ADHD, and PTSD. Assessing your specific diagnosis is crucial in determining the most suitable therapy.
Treatment History: If traditional treatments have been ineffective, TMS may be considered, especially for treatment-resistant depression. Neurofeedback offers an alternative for those seeking non-pharmacological interventions or wishing to enhance self-regulation skills.
Personal Preferences: Some individuals prefer the passive nature of TMS sessions, while others may value the active participation required in Neurofeedback training. Understanding your comfort level and engagement preferences can guide your choice.
Accessibility and Cost
Availability: TMS requires specialized equipment and is typically administered in clinical settings, which may limit accessibility in certain areas. Neurofeedback can sometimes be conducted at home with proper guidance, offering more flexibility.
Cost and Insurance Coverage: TMS therapy costs can range between $5,000 and $10,000 for a full treatment course. Many insurance companies cover TMS for depression, making it more affordable for insured patients. In contrast, Neurofeedback is often less expensive per session but usually requires numerous sessions, and insurance coverage is less common. It's essential to consult with your insurance provider to understand coverage specifics.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
Before deciding on a treatment plan, consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is imperative. They can provide a comprehensive assessment of your condition, discuss the potential benefits and limitations of each therapy, and recommend a personalized approach tailored to your needs. At The Forge Recovery Center, our team is dedicated to guiding you through this decision-making process, ensuring you receive the most effective and appropriate care for your journey toward recovery.
By carefully considering these factors and seeking professional advice, you can make an informed choice between TMS and Neurofeedback, aligning your treatment with your specific circumstances and goals.
TMS or Neurofeedback: Which Path Will You Choose?
In this article, we've explored the definitions, mechanisms, applications, procedures, and comparative effectiveness of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Neurofeedback therapies. Understanding these facets is crucial in determining the most suitable treatment for your mental health needs.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we recognize that each individual's journey is unique. Our dedicated team is here to guide you through exploring TMS, Neurofeedback, and other therapeutic options, crafting a personalized plan to support your recovery. Reach out to us today to take the first step toward a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772





