TMS Therapy Vs. ECT Comparing Treatment Methods


Wondering how TMS therapy compares to ECT? Discover key differences, benefits, and which is right for you. Find the best TMS therapy near me today!
Mental health challenges can feel overwhelming, especially when traditional treatments don’t provide relief. If you or a loved one is struggling with severe depression or other mental health conditions, alternative therapies like Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) may offer hope.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we understand the importance of finding effective, personalized treatment options. Whether you’re searching for the best TMS therapy near me or exploring other solutions, understanding the differences between TMS and ECT is crucial. In this article, we will compare these two treatments to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding TMS Therapy
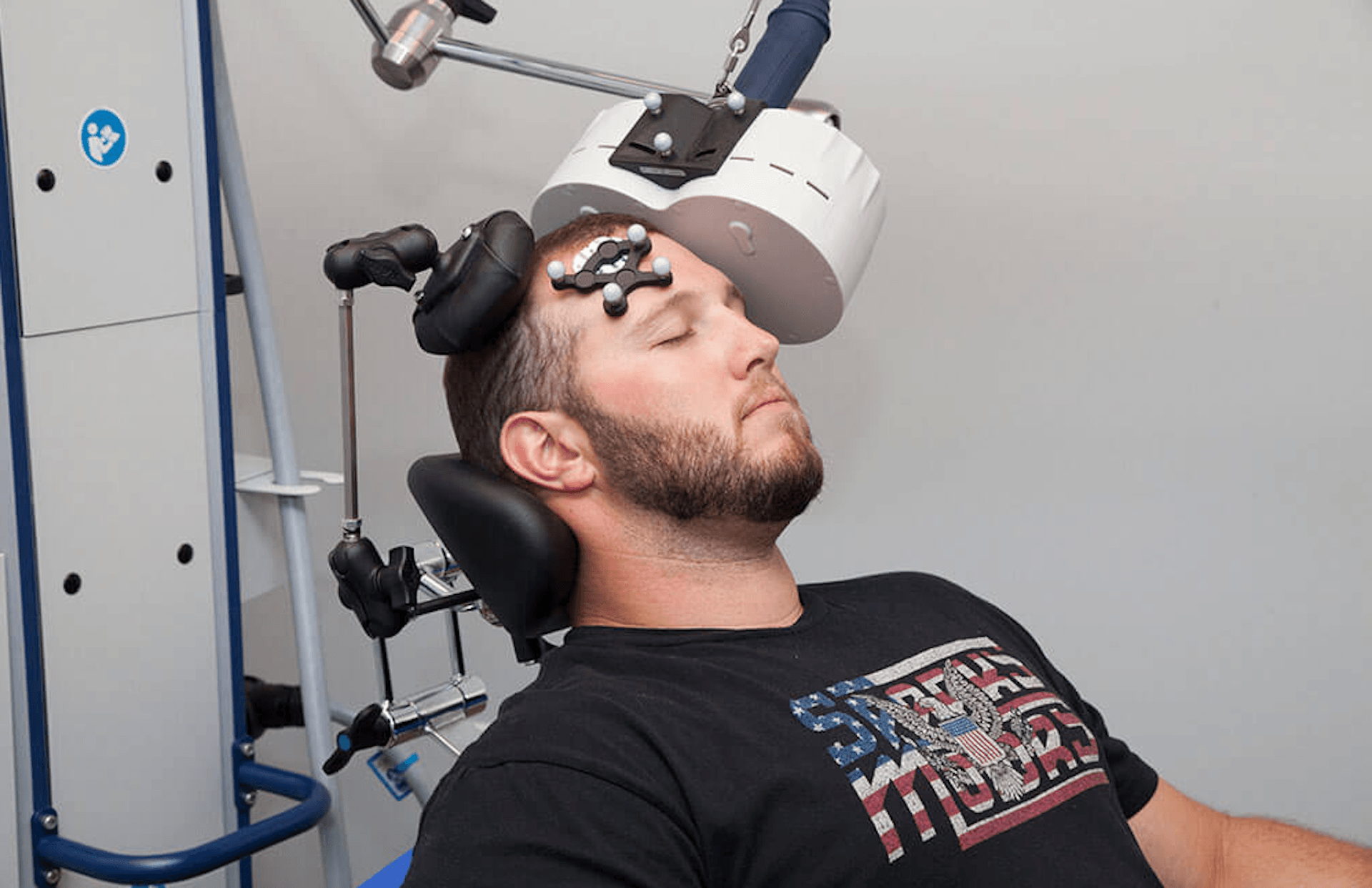
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive, FDA-approved treatment that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. This therapy is primarily used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD) and other mental health conditions when standard treatments, such as medication and therapy, haven’t been effective.
TMS works by delivering pulsed magnetic fields to specific areas of the brain involved in mood regulation, particularly the prefrontal cortex. These pulses generate small electrical currents that help reactivate underactive neurons, improving symptoms of depression over time. Unlike Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT), TMS does not cause seizures or require sedation, making it a gentler option for many individuals.
Procedure
One of the biggest advantages of TMS therapy is its non-invasive and outpatient nature. A typical TMS session involves:
The patient sits comfortably in a treatment chair.
A technician places a coil over the scalp, positioned to target the brain’s mood-regulating areas.
Magnetic pulses are delivered in short bursts, usually lasting 30–40 minutes per session.
The patient remains awake and alert, experiencing only mild tapping sensations on the scalp.
After the session, patients can immediately resume normal activities, including driving and working.
TMS therapy is usually administered five days a week for four to six weeks, depending on individual needs. Since it does not involve medication, TMS is often a preferred option for those who experience intolerable side effects from antidepressants.
Indications
TMS therapy is primarily used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), especially in patients who have not responded to traditional treatments. However, it is also being studied and used for other conditions, including:
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD)
Anxiety disorders (including generalized anxiety and OCD)
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Bipolar depression
Chronic pain conditions (such as fibromyalgia)
At The Forge Recovery Center, we understand that finding the right treatment can be challenging. If you’re searching for the best TMS therapy near me, our team is here to guide you through the process and help you determine if TMS is the right option for your mental health journey.
Understanding ECT (Electroconvulsive Therapy)

Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical procedure that uses controlled electrical currents to induce brief seizures in the brain. This treatment is designed to alter brain chemistry and can provide rapid relief for individuals with severe or treatment-resistant mental health conditions.
ECT is one of the most effective options for severe depression and is often used when other treatments, such as medications and therapy, have failed. Research suggests that the electrical stimulation triggers neurochemical changes that can help restore normal brain function, particularly in individuals experiencing severe mood disorders, psychosis, or acute suicidality.
Unlike TMS, which uses magnetic fields, ECT directly stimulates brain activity and typically leads to faster symptom relief, especially in critical cases.
Procedure
Unlike TMS, ECT is an invasive procedure that requires general anesthesia and close medical supervision. A standard ECT session includes the following steps:
Anesthesia and Muscle Relaxants – The patient is placed under general anesthesia, and a muscle relaxant is administered to prevent physical convulsions.
Electrode Placement – Electrodes are positioned on the patient’s scalp, either on one side (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral) of the head.
Electrical Stimulation – A controlled electric current is passed through the brain, inducing a brief seizure lasting 30 to 60 seconds.
Monitoring and Recovery – The patient is closely monitored during and after the procedure, typically waking up within 5 to 10 minutes. Most patients stay in a recovery area for about an hour before going home.
ECT is typically performed two to three times per week, with a total of six to twelve sessions depending on the severity of symptoms and patient response. While it can provide rapid symptom relief, some individuals experience temporary memory loss or confusion after treatment.
Indications
ECT is recommended for individuals experiencing severe psychiatric conditions that have not responded to traditional treatments. These include:
Severe Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) – Especially when accompanied by psychotic symptoms, catatonia, or severe functional impairment.
Treatment-Resistant Depression (TRD) – Patients who have tried multiple antidepressants and therapies without improvement.
Bipolar Disorder – Particularly for bipolar depression and severe manic episodes.
Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders – When symptoms include catatonia or severe delusions.
Acute Suicidality – ECT is sometimes used in emergency cases where immediate symptom relief is critical.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we understand the importance of exploring all available treatment options for mental health recovery. While ECT can be highly effective for certain conditions, it also comes with risks and side effects that should be carefully considered. If you’re searching for the best TMS therapy near me as a less invasive alternative, our team can help determine the right treatment plan based on your unique needs.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Efficacy Comparison: TMS Therapy Vs. ECT
When deciding between Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT), understanding their effectiveness is crucial. Both treatments have shown success in treating major depressive disorder (MDD) and other severe mental health conditions, but they differ in their approach, response rates, and long-term impact.
TMS Therapy: How Effective Is It?
TMS therapy has been proven effective for individuals with treatment-resistant depression (TRD)—people who have not responded to at least two antidepressant medications. Studies indicate that:
50-60% of patients with TRD show a meaningful improvement in depressive symptoms after completing TMS treatment.
About one-third of patients achieve full remission, meaning their depression symptoms disappear entirely.
Long-term benefits are seen in many patients, especially when followed by maintenance therapy or continued psychiatric support.
Unlike ECT, TMS does not require anesthesia or induce seizures, making it a more appealing option for those who want a non-invasive alternative with minimal side effects. However, TMS therapy takes longer to show noticeable improvements, with most patients experiencing relief after four to six weeks of regular sessions.
ECT: A Faster but More Intensive Solution
ECT is considered one of the most effective treatments for severe depression, particularly when symptoms are life-threatening. Research has found that:
70-90% of patients with severe or treatment-resistant depression experience significant improvement with ECT.
It is often the fastest-acting treatment, with many patients experiencing symptom relief after just a few sessions.
It is especially effective for acute suicidality, psychotic depression, and bipolar disorder, where rapid intervention is needed.
However, ECT comes with notable drawbacks. Memory loss and cognitive side effects are common, with some patients experiencing short-term or even long-term memory issues. Additionally, because it requires general anesthesia, hospital visits, and a longer recovery time, ECT is less convenient than TMS for many patients.
Which Treatment Is Right for You?
Both TMS and ECT have high success rates, but the right choice depends on your condition, treatment history, and personal preferences.
If you need a non-invasive, outpatient treatment with minimal side effects, TMS therapy may be the better option.
If you are facing severe, life-threatening depression or acute suicidality, ECT may provide faster, more immediate relief.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we help individuals explore personalized treatment plans based on their unique needs. If you’re searching for the best TMS therapy near me, our team is ready to guide you toward the most effective, least disruptive treatment path for your mental health journey.
Side Effects and Safety: TMS Therapy Vs. ECT
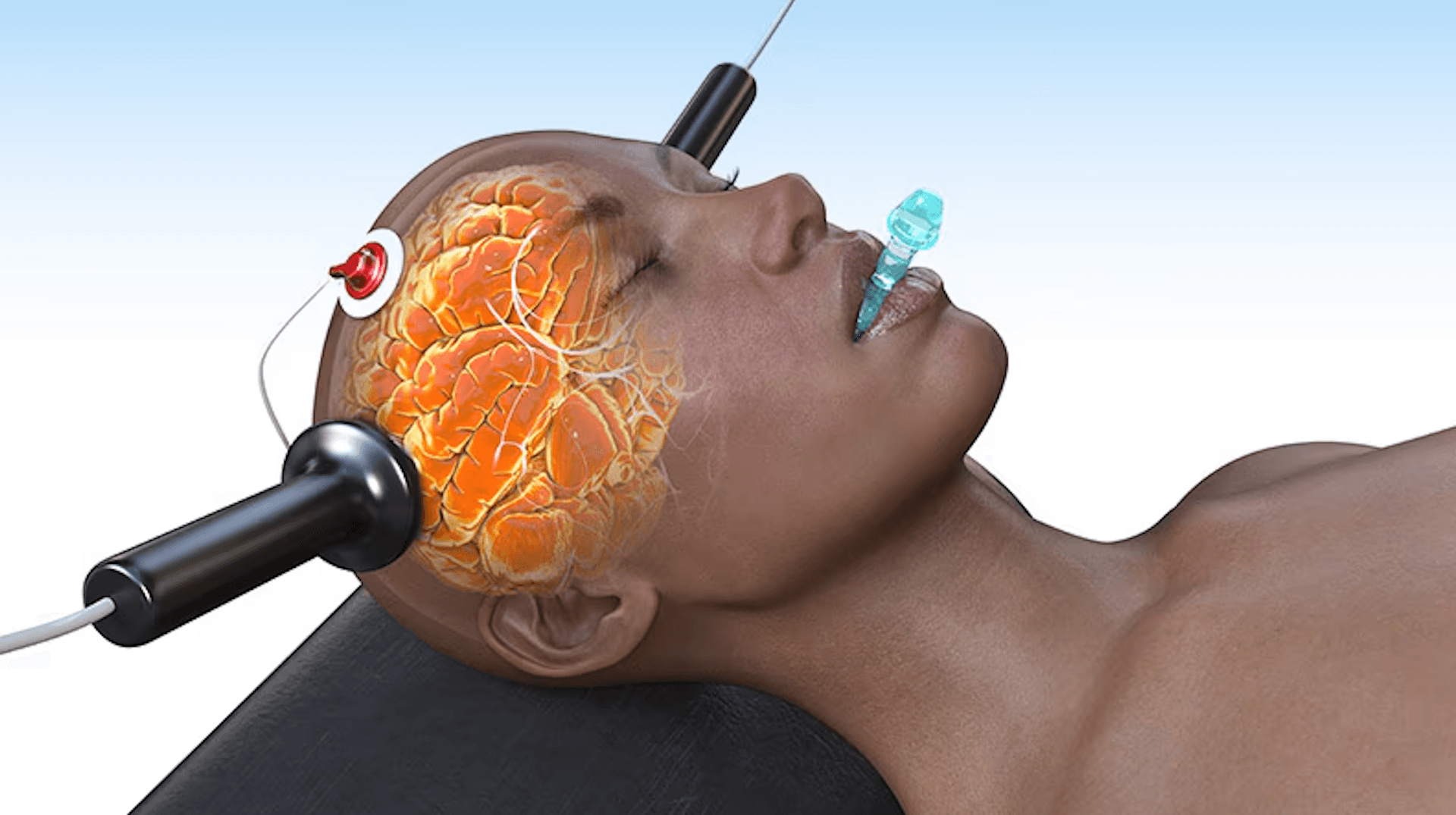
When choosing between Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), it’s essential to consider not only their effectiveness but also their side effects and overall safety. Both treatments impact brain activity but differ significantly in their potential risks and recovery process.
TMS Therapy: Mild and Temporary Side Effects
One of the main advantages of TMS therapy is its non-invasive nature and minimal side effects compared to other depression treatments. Since TMS does not require anesthesia, hospitalization, or induce seizures, it is generally considered a safe and well-tolerated option.
Common side effects of TMS include:
Mild headaches – Often temporary and improve after a few sessions.
Scalp discomfort – A slight tingling or tapping sensation during treatment, which fades over time.
Lightheadedness – Some patients experience mild dizziness immediately after the session.
Facial twitching – In rare cases, muscle contractions in the face may occur but typically stop after adjusting the device settings.
Serious side effects are extremely rare, with the most significant risk being seizures, which occur in less than 0.1% of cases. TMS is generally safe for most individuals, except those with metal implants, pacemakers, or a history of seizures, who should consult a specialist before treatment.
ECT: More Significant Side Effects and Risks
ECT is a more intensive treatment that involves general anesthesia and induces controlled seizures to stimulate brain activity. While highly effective for severe depression, its side effects can be more pronounced and sometimes long-lasting.
Common side effects of ECT include:
Short-term memory loss – Many patients experience difficulty recalling recent events for days or weeks after treatment.
Confusion and disorientation – Especially in older adults, with symptoms typically resolving within a few hours.
Physical side effects from anesthesia – Including nausea, muscle soreness, and headaches after each session.
Cognitive impairments – Some individuals report difficulty with concentration or recalling information, which may persist for weeks or months in rare cases.
Although serious complications from ECT are uncommon, the risks associated with anesthesia and seizure induction make it a more invasive treatment than TMS. Due to its intensity, ECT is usually reserved for severe or life-threatening cases of depression where faster results are needed.
Which Treatment Is Safer?
TMS therapy is generally safer and has fewer side effects, making it a better choice for individuals seeking a low-risk, outpatient treatment.
ECT is highly effective but comes with more significant risks, particularly in terms of memory loss and cognitive side effects.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we prioritize safe, effective treatments tailored to each individual. If you’re looking for the best TMS therapy near me, our expert team is here to help you explore the safest and most effective treatment options for your mental health recovery.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Accessibility and Convenience: TMS Therapy Vs. ECT
When considering a mental health treatment, accessibility and convenience play a crucial role. While both transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be effective, they differ significantly in their time commitment, treatment setting, and recovery process.
TMS Therapy: A Convenient Outpatient Treatment
TMS therapy is designed to be easily accessible and fits into most patients' daily routines. It is:
Performed in an outpatient setting – No hospitalization or intensive care is required.
Quick and efficient – Each session lasts about 30 to 40 minutes, making it easy to fit into a busy schedule.
Frequent but manageable – Typically administered five times a week for four to six weeks.
Immediate recovery – Patients can return to work, drive, and resume daily activities immediately after each session.
Because TMS is non-invasive and does not require anesthesia, it is a low-disruption treatment option for individuals seeking a safe and effective way to manage depression without needing hospitalization.
ECT: More Intensive and Time-Consuming
ECT, on the other hand, requires a greater time commitment and a more intensive treatment process. It is:
Usually performed in a hospital or specialized clinic – It may require inpatient care or intensive outpatient visits.
Less frequent but more demanding – Sessions typically occur two to three times a week for several weeks.
Recovery takes longer – Since ECT involves general anesthesia, patients may experience grogginess, confusion, or temporary memory loss for several hours after each session.
Requires assistance – Patients are often advised not to drive or work immediately after treatment, meaning they may need support from family or caregivers.
While ECT is effective, its higher level of medical supervision, hospital visits, and recovery time makes it a less convenient option for individuals who need a treatment that fits into their daily life.
Which Treatment Is More Accessible?
TMS therapy is the more convenient option for most people, as it allows patients to continue their daily activities with minimal disruption.
ECT requires hospitalization or intensive outpatient care, making it less accessible for individuals who cannot afford extended recovery periods.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we understand that accessibility is key to successful treatment. If you’re looking for the best TMS therapy near me, our team is here to provide personalized, outpatient mental health care that fits into your life while delivering lasting results.
TMS or ECT? Find the Right Treatment for You
Both TMS therapy and ECT offer effective solutions for treatment-resistant depression, but they differ in invasiveness, side effects, and convenience. TMS is non-invasive, has minimal side effects, and allows patients to resume daily activities immediately, while ECT is more intensive, requiring anesthesia and longer recovery.
At The Forge Recovery Center, we believe in personalized treatment plans tailored to your needs. If you’re unsure which option is right for you, our team is here to help. Reach out today to explore the best path to recovery and lasting mental wellness.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772





