Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Understanding, Diagnosing & Treatment


Obsessive-compulsive disorder, commonly known as OCD, has a history deeply intertwined with human understanding of mental health. Dating back to ancient times, individuals struggling with OCD symptoms faced stigma and misunderstanding. However, advancements in psychology and neuroscience have shed light on this complex anxiety disorder.
Understanding OCD: What Is Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder?
OCD is a mental health condition characterized by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions). Obsessions are unwanted, persistent thoughts, images, or impulses that cause significant distress. Compulsions are repetitive behaviors or mental acts that individuals feel driven to perform in response to obsessions.
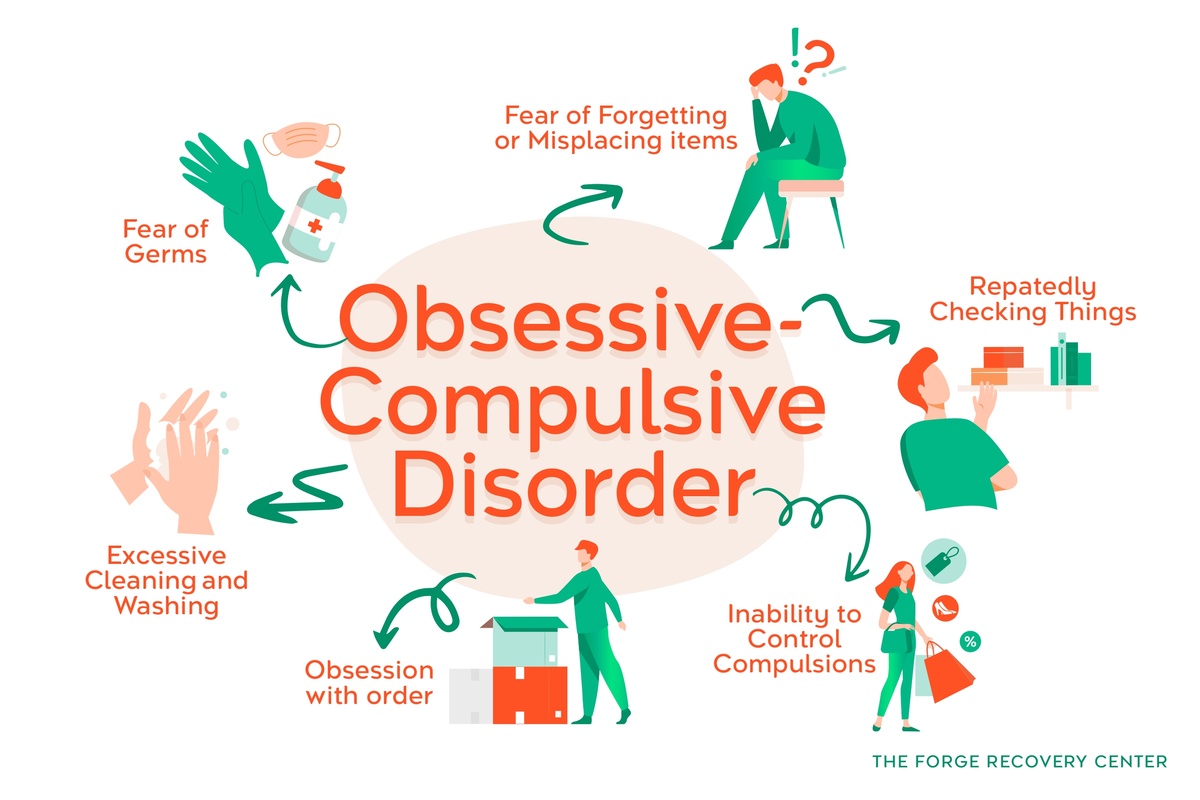
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Defined
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is characterized by obsessional thoughts and compulsive behaviors that individuals feel driven to perform. These obsessions are intrusive and unwanted, causing significant distress. The compulsions are repetitive actions or mental rituals that temporarily reduce anxiety but must be repeated excessively.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder can severely impact daily life, leading to disruptions in work, relationships, and overall functioning. Treatment options for managing OCD include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), medication such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and exposure and response prevention therapy.

What Are the Symptoms of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder?
The main symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder are intrusive, unwanted thoughts and repetitive behaviors or mental rituals. These symptoms can significantly interfere with daily life, causing distress and affecting relationships, work, and functioning.
Behavioral Signs of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Common obsessions in OCD include fears of contamination, doubts about safety, and a need for symmetry or exactness. Compulsions often manifest as repetitive actions like handwashing, checking locks repeatedly, or counting items compulsively. Individuals with OCD may spend hours each day performing these rituals to alleviate anxiety and prevent perceived harm.
Emotional Indicators of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
The symptoms of OCD can lead to intense emotional distress, including feelings of fear, guilt, or shame. Obsessions trigger overwhelming anxiety in individuals with OCD, compelling them to engage in compulsive behaviors to reduce their distress. Moreover, the emotional need for order and symmetry can drive individuals with OCD to arrange items meticulously or perform rituals until they feel a sense of completeness.
Physical Symptoms of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
The physical symptoms of OCD are often a result of compulsive behaviors. For example, frequent handwashing can cause skin irritation and dryness, while repetitive actions like counting or tapping can lead to muscle strain and fatigue. In severe cases, individuals may experience injuries from compulsions, such as cuts or bruises from excessive cleaning or organizing.
Cognitive Symptoms of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Individuals with OCD may also experience cognitive symptoms such as difficulty concentrating and making decisions. Obsessions can be distracting and overwhelming, leading to a preoccupation with repetitive thoughts or rituals that interfere with daily tasks.
How Does Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Affect Relationships?
OCD can significantly impact relationships, as individuals may require excessive reassurance or be unable to engage in activities due to their symptoms. This can lead to feelings of frustration and isolation for both the person with OCD and their loved ones.
Moreover, obsessions may involve irrational fears that can strain relationships. For example, a fear of germs may cause a person with OCD to avoid physical contact or sharing personal items, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts.

Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Treatment Options for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
The good news is that OCD is a treatable disorder. With proper diagnosis and individualized treatment, many people with OCD can significantly reduce their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is the most common form of psychotherapy used to treat OCD. This therapy approach focuses on identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. Through CBT, individuals learn coping strategies to manage their symptoms and gradually reduce the frequency and intensity of obsessions and compulsions.
Medications
Medications can be an effective treatment option for individuals with OCD, particularly in combination with psychotherapy. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed medications, which can help regulate neurotransmitters in the brain that are associated with mood and anxiety.
Brain Stimulation Therapies
For individuals who do not respond to traditional treatment methods, brain stimulation therapies may be a viable option. This includes transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), which involves stimulating specific areas of the brain to improve symptoms of OCD.
Treatment Overview: How Is Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Treated?
OCD is a chronic condition that requires long-term management. However, with proper treatment, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Psychotherapy Benefits
Psychotherapy offers significant benefits in treating OCD by helping patients understand and manage their symptoms. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), a common psychotherapy approach, focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It assists individuals in recognizing triggers for obsessions and compulsions.
Moreover, psychotherapy plays a crucial role in managing obsessions and compulsions by teaching patients coping mechanisms and relaxation techniques. This therapy helps individuals develop strategies to resist engaging in compulsive behaviors, leading to improved quality of life.
Medication Options
Various medication options exist for treating OCD, with SSRIs being commonly prescribed due to their effectiveness in reducing symptoms. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) help regulate serotonin levels in the brain, which can alleviate obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
Medication plays a vital role in reducing OCD symptoms, especially when combined with psychotherapy. It can provide relief for patients experiencing severe distress from their obsessive-compulsive symptoms, improving their overall well-being.
Alternative Approaches
In addition to traditional treatments, alternative approaches offer additional avenues for managing OCD symptoms. Complementary therapies such as mindfulness meditation and yoga have shown promise in reducing anxiety levels associated with OCD. These approaches focus on promoting relaxation and stress reduction.
Exploring different treatment options is essential in managing OCD effectively. By considering alternative approaches alongside conventional treatments, individuals can tailor their treatment plans to suit their unique needs. This holistic approach enhances the overall treatment outcome for patients struggling with OCD.

Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a key psychotherapeutic approach for individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). It focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. CBT helps individuals develop insight into their condition, identifying triggers for intrusive thoughts.
How Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Works
By challenging irrational beliefs, individuals can learn coping strategies to manage OCD symptoms effectively. The therapy typically involves structured sessions where individuals work with therapists to gradually confront their fears and reduce compulsive behaviors. Studies have shown that CBT is highly effective in reducing OCD symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
Exposure Response Prevention
Exposure response prevention (ERP) is another crucial form of psychotherapy used to treat OCD. This therapy involves exposing individuals to situations that trigger obsessions while preventing them from engaging in compulsive rituals. Through repeated exposure to feared stimuli, individuals learn that their anxiety decreases over time without performing compulsions.
ERP aims to break the cycle of obsessions and compulsions by helping individuals tolerate distress without resorting to rituals. Therapists guide individuals through gradual exposure exercises, supporting them in confronting their fears and resisting the urge to perform compulsions.
Medication and Management for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Medication can be helpful in treating the symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
SSRIs and Effects
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). They help by increasing serotonin levels in the brain, which regulate mood and behavior. SSRIs like fluoxetine (Prozac) or sertraline (Zoloft) can effectively reduce OCD symptoms. However, these medications may take several weeks to show noticeable improvements.
However, the potential side effects of SSRIs in treating OCD include nausea, insomnia, headaches, and sexual dysfunction. It's crucial for individuals to discuss any adverse effects with their healthcare provider to adjust the dosage or consider alternative medications.
Managing Side Effects
To manage the side effects of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) medications, individuals can adopt various strategies. These include taking the medication with food to minimize stomach discomfort, adjusting the dosage under medical supervision, or trying different timing schedules. Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or mindfulness can alleviate some side effects.
Monitoring and promptly communicating any side effects with healthcare providers, mental health professionals, or the provider is essential for successful treatment. It’s crucial to address concerns related to significant distress, an increase in symptoms, or any unwanted effects. Additionally, staying informed about neuropsychiatric disorders, neurological disorders, and the specific brain areas affected by OCD can guide treatment decisions.
A Combination of Treatment
Remember that effective treatment often involves a combination of medication, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other evidence-based interventions. For young adults, individuals, and patients dealing with OCD, seeking help from a doctor, mental health professional, or healthcare provider is essential. Whether it’s deep brain stimulation, behavioral therapy, or antidepressant medications, a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to each person’s needs can lead to improved functioning, better quality of life, and reduced distress.
In severe cases, where common compulsions, common obsessions, or intrusive thoughts significantly impact daily life, exploring surgical procedures or alternative therapies may be necessary. The future of OCD treatment continues to evolve, with ongoing research and advancements in understanding the underlying causes and conditions.
Remember, you’re not alone, and seeking help is a sign of strength. Reach out to a mental health professional, and together, we can work toward managing OCD and promoting well-being.

Lifestyle and Coping Strategies for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Making lifestyle adjustments can be very helpful in treating obsessive-compulsive disorder as well.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress reduction techniques play a crucial role in managing obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) symptoms. Engaging in activities like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help individuals alleviate anxiety and reduce the intensity of obsessive thoughts. These practices promote relaxation and calmness, aiding in better coping with OCD triggers.
Incorporating relaxation techniques into daily routines is essential for individuals with OCD. Whether it’s practicing mindfulness, following guidelines for stress management, or seeking support from mental health professionals, these strategies contribute to improved well-being and overall functioning.
Remember that seeking help and building a strong support network are essential steps on the path to managing OCD.
Support Networks
Building a strong support network is vital for individuals dealing with OCD. Family members, friends, therapists, and support groups can offer emotional understanding and practical assistance to those struggling with the disorder. Having a support system in place provides individuals with a safe space to express their feelings and concerns without judgment.
Support networks play a significant role in connecting individuals with OCD to others who share similar experiences. Support groups create a sense of community where individuals can exchange coping strategies, share success stories, and provide mutual encouragement. This connection helps combat feelings of isolation and fosters a sense of belonging among those affected by OCD.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
What Causes Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder?
While the exact cause of OCD is unknown, research suggests that a combination of biological, environmental, and psychological factors may contribute to its development. These can include genetics, brain chemistry, childhood experiences, and life events.
Genetic Links
Genetics plays a significant role in the development of OCD, with studies indicating a hereditary component. Individuals with a first-degree relative who has OCD have a higher risk of developing the disorder themselves. Brain imaging studies have shown structural and functional differences in the brains of individuals with OCD compared to those without the condition.
Environmental Triggers
Childhood trauma, such as abuse or neglect, can contribute to the onset of OCD later in life. Environmental factors like stress or traumatic events can worsen existing symptoms or trigger the development of new ones. Negative emotions experienced during childhood may increase the risk of developing OCD in adulthood by influencing brain function and emotional regulation mechanisms.
Neurological Causes
Research suggests that changes in brain chemistry, specifically involving the neurotransmitter serotonin, may play a role in OCD. Serotonin helps regulate mood and behavior, and imbalances can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders like OCD.
Behavioral Causes
Certain behaviors, such as excessive hand washing or checking, can become compulsive and reinforce the symptoms of OCD. Over time, these behaviors can become habitual and difficult to control.
Cognitive Causes
Individuals with OCD often have distorted thinking patterns, leading to irrational beliefs and exaggerated fears. These thoughts can contribute to the development and maintenance of OCD symptoms.

Diagnosing OCD: How Is Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of OCD involves a comprehensive assessment, incorporating medical history, psychological evaluations, and diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). A qualified mental health professional will conduct a thorough evaluation to determine if an individual meets the criteria for OCD.
Professional Assessment
Seeking professional evaluation for OCD is crucial to receiving an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Healthcare providers, including psychologists and psychiatrists, play a significant role in diagnosing OCD. They conduct thorough assessments to identify symptoms and determine the presence of compulsive disorder or anxiety disorders. Referral to a mental health professional is often necessary for a comprehensive evaluation.
Diagnostic Criteria
Diagnosing OCD can be challenging due to its overlapping symptoms with other mental health conditions. To meet the diagnostic criteria for OCD, individuals must experience obsessions - intrusive thoughts or urges - and engage in compulsions - repetitive behaviors. These obsessions and compulsions cause distress and significantly impact daily functioning. Meeting specific criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) is essential for an accurate diagnosis.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
How Does Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Impact Relationships?
OCD can have a significant impact on relationships, as the symptoms and behaviors associated with the disorder can create difficulties in communication and understanding. This can lead to strain and conflict between partners, family members, and friends.
Social Interactions
Individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) often experience challenges in social interactions. The constant worries and concerns about cleanliness, safety, or orderliness can lead to avoidance of social situations. This avoidance can cause significant distress and isolation.
People with OCD may find it hard to engage in spontaneous activities due to their rituals or intrusive thoughts. This can make them appear distant or preoccupied in social settings. Their need for reassurance or repetitive behaviors can be misunderstood by others, leading to strained relationships.
Understanding the impact of OCD on social interactions is crucial for providing appropriate support. Encouraging open communication and patience can help individuals with OCD feel accepted and understood. Educating friends and family members about the disorder can foster empathy and reduce stigma.
Family Dynamics
Family dynamics play a vital role in the development and management of OCD. Family support can significantly influence how individuals cope with their symptoms. A supportive environment that acknowledges the challenges of OCD can create a sense of safety and understanding for the affected individual.
On the other hand, negative family dynamics, such as criticism or lack of understanding, can exacerbate OCD symptoms. Family members' reactions to the rituals or compulsions may inadvertently reinforce these behaviors. Therefore, involving family members in therapy sessions or support groups can enhance treatment outcomes.
Family members also play a crucial role in helping individuals with OCD navigate daily life. Providing encouragement, participating in treatment plans, and offering emotional support are essential aspects of managing OCD within a family unit.
Seeking Professional Help
Taking the first step to treatment isn’t easy…but it’s worth it. OCD is a treatable condition that responds well to treatment.
Finding Therapists
Finding the right mental health professional is crucial for individuals dealing with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). It is essential to seek out therapists who specialize in OCD treatment to ensure effective care. When looking for a therapist, consider their experience in treating OCD specifically.
Therapists experienced in OCD are better equipped to provide appropriate strategies and support tailored to the individual's needs. Therapy plays a vital role in the long-term management of OCD by helping individuals understand their condition, develop coping mechanisms, and work towards reducing symptoms over time.
Clinical Trials Importance
Participating in clinical trials can be significant for advancing research on OCD. Clinical trials contribute to expanding knowledge about effective treatment options for OCD by testing new therapies and interventions. Individuals with OCD who participate in clinical trials not only contribute to scientific progress but also have the potential to access cutting-edge treatments before they become widely available.
The benefits of engaging in clinical trials include receiving specialized care from experts in the field and contributing to improving future treatment outcomes for individuals with OCD.

Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
What Happens if Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Is Untreated?
If left untreated, OCD can significantly impair an individual's daily life and overall well-being. The symptoms may worsen over time, making it challenging to maintain relationships, hold a job, or engage in enjoyable activities.
Furthermore, untreated OCD can lead to the development of other mental health disorders such as depression and substance abuse as individuals may turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms to manage their symptoms.
Long-Term Complications
Affected individuals with untreated OCD may experience severe long-term complications. Over time, unwanted thoughts can escalate, leading to increased anxiety and distress. These persistent symptoms can significantly impair daily functioning.
The impact of untreated OCD extends beyond mental health. Individuals may face challenges in maintaining relationships, holding employment, and pursuing personal goals. The constant battle with intrusive thoughts can result in social isolation and reduced quality of life.
Early intervention is crucial in preventing the progression of OCD symptoms and mitigating long-term consequences. Seeking professional help at the onset of symptoms can lead to better management strategies and improved overall well-being.
Importance of Early Treatment
Early treatment for OCD offers several advantages for affected individuals. Prompt intervention can prevent the future exacerbation of symptoms and reduce the risk of developing additional mental health issues.
Timely treatment plays a vital role in enhancing the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions. Individuals who receive early support are more likely to respond well to cognitive-behavioral therapy and medication, leading to better symptom control.
Closing Thoughts
You've gained valuable insights into obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), from understanding its nature to the impact it can have on relationships. Recognizing the importance of seeking professional help, you now have a comprehensive view of the diagnosis, treatment options, and coping strategies available for managing OCD. By delving into psychotherapy, medication, lifestyle adjustments, and unaddressed consequences, you are better equipped to navigate the complexities of living with OCD or supporting someone who does.
Take proactive steps today by applying the knowledge you've acquired. Whether it's reaching out to a mental health professional, exploring therapy options, or implementing coping mechanisms in your daily life, remember that support and resources are within reach. Empower yourself with information and take charge of your journey towards managing OCD effectively.
OCD Treatment in Orange County
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is a prison of unwanted thoughts and worries. It's a uniquely isolating condition; few understand what living with untreated OCD is like. Worse, left untreated, it gets worse.
Fortunately, OCD is treatable. At The Forge Recovery Center, we use proven, effective methods to help you free yourself from the effects of OCD. Our unique approach combines therapy, medication management, and neurofeedback to help you break free from the cycle of obsessions and compulsions.
Don't let OCD control your life any longer. Contact The Forge Recovery Center today to learn more about our comprehensive treatment programs and take the first step towards reclaiming your life.



