Major Depressive Disorder: Symptoms, Causes, & Treatment


Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, causes persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest — and we understand how it can disrupt all aspects of life. But help and treatment are available, usually in the form of therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and medication if necessary. Learn more about the symptoms and treatment options for MDD, and call The Forge Recovery Center today if you or a loved one are in need of professional support.
What Is Major Depressive Disorder?
Major depressive disorder is a mental health condition characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyable. It can affect how a person thinks, feels, and behaves, leading to difficulties in daily functioning.
Symptoms of major depressive disorder may include changes in appetite or weight, sleep disturbances, fatigue, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of death or suicide. Treatment options typically include therapy, medication, or a combination of both to help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
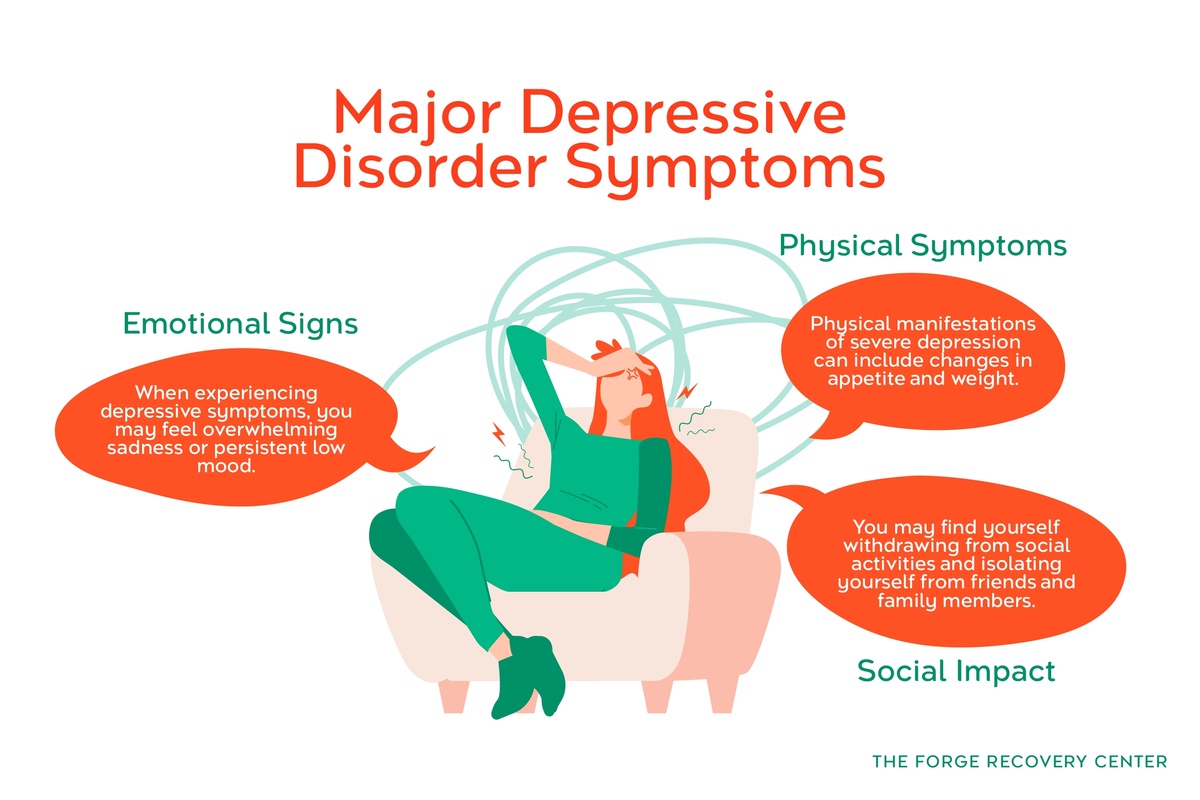
Major Depressive Disorder Symptoms
Depression carries a number of emotional and physical symptoms, which often result in certain social impacts such as isolation and disconnection. Here’s a summary of the symptoms associated with major depressive disorder:
Emotional Signs
When experiencing depressive symptoms, you may feel overwhelming sadness or persistent low mood. Your depressed mood can be intense, leading to feelings of hopelessness and worthlessness. These emotions may disrupt your daily life.
You might also notice a significant decrease in interest or pleasure in activities you once enjoyed. This loss of interest can extend to hobbies, social interactions, and even personal relationships. Depressive episodes often manifest as irritability or frustration.
Physical Symptoms
Physical manifestations of severe depression can include changes in appetite and weight. You may experience either a significant increase or decrease in appetite, leading to noticeable weight fluctuations. You might encounter issues with sleep patterns, such as insomnia or oversleeping.
Moderate depression can also manifest physically through fatigue and low energy levels. Daily tasks that were once manageable may become challenging due to persistent tiredness. Headaches, digestive problems, and muscle pains are common physical symptoms associated with depression.
Social Impact
The social impact of major depressive disorder can be profound. You may find yourself withdrawing from social activities and isolating yourself from friends and family members. This isolation can further exacerbate feelings of loneliness and contribute to a sense of disconnection.
In social settings, individuals with depression may struggle to engage fully or express themselves authentically. This difficulty in communication can lead to misunderstandings with loved ones or colleagues. Work performance may decline due to lack of concentration and motivation.

Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Treatment for Major Depressive Disorder
Treatment for major depressive disorder typically involves a combination of therapy and medication to manage symptoms. This is administered by a mental health professional, such as a mix of psychologists and psychiatrists, or at a mental health treatment center. Here’s a quick overview of how treatment proceeds:
Therapy
When seeking therapy for major depressive disorder, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a widely used approach. CBT helps you identify negative thought patterns and behaviors, replacing them with positive ones. This therapy focuses on practical solutions to improve your mood and outlook.
Psychodynamic therapy, another form of therapy, delves into your unconscious thoughts and past experiences to understand present behavior. By exploring these underlying factors, you can gain insight into your emotions and relationships, aiding in managing depressive symptoms effectively.
Medication
In treating major depressive disorder, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed antidepressants. SSRIs work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain, improving mood, and reducing symptoms of depression. These medications are often the first-line treatment due to their effectiveness and tolerability.
Another class of antidepressants known as serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) also play a crucial role in managing depression. SNRIs work by increasing levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain, regulating mood and energy levels to alleviate depressive symptoms effectively.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Making lifestyle adjustments can significantly impact your mental health. Engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, ensuring adequate sleep, and avoiding alcohol or drugs can help improve your overall well-being. These changes can complement other treatments for major depressive disorder.
Support Groups
Joining support groups can provide you with a sense of community and understanding during your journey with major depressive disorder. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can offer emotional support, coping strategies, and a safe space to express your feelings without judgment.
Mental Health Treatment Centers
For comprehensive care, considering mental health treatment centers is beneficial. These centers offer specialized programs tailored to individual needs, providing access to psychiatrists, therapists, and various treatment options under one roof. This integrated approach enhances the effectiveness of managing major depressive disorder.
What Causes Major Depressive Disorder?
Major depressive disorder is largely thought to be tied to family history, although certain biological and environmental factors can come into play as well. Let’s explore these causes further:
Family History
When it comes to major depressive disorder, your family history plays a significant role. If someone in your family has experienced depression, you may be at a higher risk. Genetic predisposition can increase susceptibility to this condition. Understanding your family's mental health history can provide valuable insights into your own risk factors.
Biological Factors
Biological factors, such as the imbalance of neurotransmitters like monoamine oxidase, can contribute to major depressive disorder. These chemicals play a crucial role in regulating mood, and any disruption can lead to depressive symptoms. Research suggests that abnormalities in brain structure and function also play a role in the development of depression.
Environmental Triggers
Your environment can also impact the onset of major depressive disorder. Stressful life events, such as the loss of a loved one, financial difficulties, or traumatic experiences, can trigger depression. Chronic stress, substance abuse, and certain medications can exacerbate symptoms. Identifying and addressing these environmental triggers is essential in managing and treating depression effectively.
Psychological Aspects
Your psychological well-being is closely linked to major depressive disorder. Negative thought patterns, low self-esteem, and unresolved emotional issues can contribute to the development of depression. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is an effective treatment approach that focuses on changing these maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors. Developing coping mechanisms and building resilience are essential aspects of managing depression effectively.
Identify negative thought patterns: Recognize when negative thoughts arise and challenge their validity.
Practice self-care: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and well-being.
Seek professional help: Therapy and medication can significantly improve symptoms.

Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Diagnosing Major Depressive Disorder
When diagnosing major depressive disorder, mental health professionals refer to the DSM to compare symptoms to criteria and use depression screening tools to further assess symptoms. A risk factor assessment may also be used to identify any genetic predispositions or environmental stressors. Here’s how the diagnosis process works:
Assessment Tools
When diagnosing major depressive disorder (MDD), healthcare professionals often refer to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). This manual provides specific criteria for identifying mental health conditions, including MDD.
Depression Screening
To screen for depression, healthcare providers may use standardized questionnaires like the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). This tool assesses various symptoms of depression, helping professionals determine the severity of the condition.
Risk Factor Assessment
In assessing risk factors for MDD, healthcare providers consider various elements that may contribute to the development or exacerbation of depression. These factors can include genetics, environmental stressors, and personal experiences.
When evaluating risk factors, it's important to consider the impact of genetic predispositions on mental health. Environmental stressors such as traumatic events or chronic illnesses can significantly increase the likelihood of developing MDD.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of an individual's risk factors for MDD, healthcare providers may also inquire about personal experiences such as history of abuse, family history of mental illness, or substance abuse.
Prevalence of Major Depressive Disorder
Global
Major depressive disorder is a significant concern worldwide. Depression affects approximately 280 million people globally, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). In many countries, the prevalence of major depressive disorder varies due to factors such as socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and cultural attitudes towards mental health. Developing nations often face challenges in providing adequate mental health services, leading to underdiagnosis and undertreatment of depression. On the other hand, developed countries may have better resources but still struggle with stigma and barriers to seeking help.
A Leading Cause of Disability
Despite the variations in prevalence rates, major depressive disorder remains a leading cause of disability worldwide. It not only affects individuals but also has broader societal implications. Addressing the global burden of depression requires collaborative efforts from governments, healthcare providers, and communities to promote awareness, improve access to treatment, and reduce stigma.
United States
In the United States, major depressive disorder is one of the most common mental health conditions, affecting millions of Americans each year. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately 21 million adults in the U.S. had at least one major depressive episode in 2021. This statistic represented 8.3% of all U.S. adults at the time, highlighting the widespread impact of depression on individuals across different age groups and backgrounds.
Interestingly, the prevalence of MDD is higher among adult females when compared to males (10.3% vs. 6.2%). Prevalence was also higher among individuals aged 18-25 (18.6%), as well as people who reported being of two or more races (13.9%).
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Seeking Help & Starting Therapy
If you’re ready to seek help and start your healing journey, your first step is reaching out to a mental health professional or treatment center that can help, alongside friends or family in your support network. Here’s some more information to aid your search for support:
Mental Health Professionals
If you’re struggling with symptoms of depression, seeking help from mental health professionals is crucial. Psychiatrists, psychologists, and licensed therapists are trained to diagnose and treat mental health conditions effectively. They can provide therapy sessions tailored to your specific needs and offer medication management if necessary.
It's essential to find a professional who specializes in major depressive disorder to ensure you receive the most appropriate care. Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medications and provide comprehensive treatment plans. Psychologists focus on therapy and counseling, helping you navigate your emotions and thoughts effectively.
Mental Health & Addiction Treatment Centers
In some cases, seeking help from a mental health or addiction treatment center may be beneficial for managing major depressive disorder. These centers offer a range of services, including therapy, support groups, and holistic treatments. They provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals struggling with mental health issues.
At these centers, you can access a multidisciplinary team of professionals, including psychiatrists, therapists, counselors, and nurses. They work together to create personalized treatment plans that address your unique needs. In addition to therapy sessions, these centers may offer recreational activities, mindfulness practices, and educational workshops to support your mental well-being.

Closing Thoughts
Now that you understand major depressive disorder, its symptoms, treatment options, causes, diagnosis, prevalence, and the importance of seeking help and starting therapy, you are equipped with valuable knowledge to navigate this mental health condition. Remember, seeking professional help is crucial in managing major depressive disorder effectively. Do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of depression. Your mental well-being is essential, and getting the support you need can make a significant difference in your journey toward healing.
Are You Struggling with Mental Health or Addiction?
We Can Help. Call Us Now!
CALL: 877-839-1772
Major Depressive Disorder Treatment in Orange County
Depression, also known as major depressive disorder (MDD), can drive persistent feelings of sadness and a loss of interest in once-loved activities. But remember, depression isn’t a sign of weakness, and you’re not alone in this struggle. At The Forge Recovery Center, we offer a team of mental health experts to guide your healing journey, alongside a range of treatment methods to support you along the way.
Call us today if you or a loved one are feeling weighed down by depressive symptoms and are ready to break free.
Treatment Modalities We Offer
At The Forge Recovery Center, we offer a range of evidence-based treatment modalities to support your healing journey, including:
Case Management
Our experts guide clients toward resources that support recovery, assessing personal risks to create a comprehensive treatment plan.
CBT
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps clients modify negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with drug addiction, aiming to prevent relapse and foster a drug-free lifestyle.
DBT
Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) assists individuals dealing with emotional instability due to substance abuse, promoting emotional regulation and positive life changes.
EMDR
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) allows clients to process trauma that may impact their addiction, using eye movement techniques to reduce psychological distress.
Experiential
Rekindle life’s joys and confront the underlying trauma of addictive behaviors through engaging in therapeutic activities.
Family Counseling
Family counseling strengthens bonds and nurtures a supportive network crucial for sustained recovery and abstinence.
Group Therapy
Group sessions provide a communal space for support, enhancing recovery through shared experiences and collective resilience.
Individual Therapy
Tailored sessions address the unique challenges faced by each client, supporting their journey toward a substance-free life.
MAT
MAT combines approved medications with counseling to effectively combat addiction, easing withdrawal symptoms and reducing relapse risk.
TMS
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), a non-invasive technique, uses magnetic fields to stimulate the brain, helping reduce intense drug cravings.
Motivational Interviewing
Motivational interviewing encourages clients to make healthier choices, such as overcoming substance use, by fostering self-efficacy.
Trauma-Informed Care
Recognizing trauma’s impact on addiction, this approach effectively guides clients through treatment, addressing its effects on mental and emotional well-being.



